| Issue |
A&A
Volume 619, November 2018
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | L7 | |
| Number of page(s) | 7 | |
| Section | Letters to the Editor | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201833513 | |
| Published online | 20 November 2018 | |
Letter to the Editor
A possible observational bias in the estimation of the virial parameter in virialized clumps
1
IAPS-INAF, Via Fosso del Cavaliere, 100, 00133
Rome, Italy
e-mail: alessio.traficante@inaf.it
2
Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Université Paris Diderot, UMR 7154 CNRS, 75005
Paris, France
3
Laboratoire AIM, Paris-Saclay, CEA/IRFU/SAp – CNRS – Université Paris Diderot, 91191
Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France
4
Haystack Observatory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 99 Millstone Road, Westford, MA, 01886, USA
5
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf Dem Hügel 69, Bonn, 53121, Germany
6
Institute for Astrophysical Research, Boston University, 725 Commonwealth Ave, Boston, MA, 02215, USA
Received:
28
May
2018
Accepted:
29
October
2018
The dynamics of massive clumps, the environment where massive stars originate, is still unclear. Many theories predict that these regions are in a state of near-virial equilibrium, or near energy equi-partition, while others predict that clumps are in a sub-virial state. Observationally, the majority of the massive clumps are in a sub-virial state with a clear anti-correlation between the virial parameter αvir and the mass of the clumps Mc, which suggests that the more massive objects are also the more gravitationally bound. Although this trend is observed at all scales, from massive clouds down to star-forming cores, theories do not predict it. In this work we show how, starting from virialized clumps, an observational bias is introduced in the specific case where the kinetic and the gravitational energies are estimated in different volumes within clumps and how it can contribute to the spurious αvir-Mc anti-correlation in these data. As a result, the observed effective virial parameter 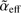 < αvir, and in some circumstances it might not be representative of the virial state of the observed clumps.
< αvir, and in some circumstances it might not be representative of the virial state of the observed clumps.
Key words: stars: massive / methods: data analysis / surveys / stars: kinematics and dynamics
© ESO 2018
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


