| Issue |
A&A
Volume 528, April 2011
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A100 | |
| Number of page(s) | 16 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201016110 | |
| Published online | 08 March 2011 | |
Zooming into the broad line region of the gravitationally lensed quasar QSO 2237 + 0305 ≡ the Einstein Cross
III. Determination of the size and structure of the C iv and C iii] emitting regions using microlensing⋆
1
Astronomisches Rechen-Institut am Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Mönchhofstrasse 12-14, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany
e-mail: sluse@ari.uni-heidelberg.de
2
Laboratoire d’Astrophysique, Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Observatoire de Sauverny, 1290 Versoix, Switzerland
3
F.R.S.-FNRS, Institut d’Astrophysique et de Géophysique, Université de Liège, Allée du 6 Août 17, B5c, 4000 Liège, Belgium
4
Centro de Astro-Ingeniería, Departamento de Astronomía y Astrofísica, P. Universidad Católica de Chile, Casilla 306, Santiago, Chile
5
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany
6
Astronomy Department, University of Washington, Box 351580, Seattle, WA 98195, USA
Received: 9 November 2010
Accepted: 13 December 2010
Aims. We aim to use microlensing taking place in the lensed quasar QSO 2237 + 0305 to study the structure of the broad line region (BLR) and measure the size of the region emitting the C iv and C iii] lines.
Methods. Based on 39 spectrophotometric monitoring data points obtained between Oct. 2004 and Dec. 2007, we derived lightcurves for the C iv and C iii] emission lines. We used three different techniques to analyse the microlensing signal. Different components of the lines (narrow, broad, and very broad) were identified and studied. We built a library of the simulated microlensing lightcurves that reproduce the signal observed in the continuum and in the lines provided only the source size is changed. A Bayesian analysis scheme is then developed to derive the size of the various components of the BLR.
Results. 1. The half-light radius of the region emitting the C iv line is found to be 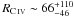 light-days = 0.06
light-days = 0.06 pc = 1.7
pc = 1.7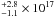 cm (at 68.3% CI). Similar values are obtained for C iii]. Relative sizes of the carbon-line and V-band continuum emitting-regions are also derived with median values of Rline/Rcont in the range 4 to 29, depending on the FWHM of the line component. 2. The size of the C iv emitting region agrees with the radius-luminosity relationship derived from reverberation mapping. Using the virial theorem, we derive the mass of the black hole in QSO 2237 + 0305 to be MBH ~ 108.3 ± 0.3 M⊙. 3. We find that the C iv and C iii] lines are produced in at least 2 spatially distinct regions, the most compact one giving rise to the broadest component of the line. The broad and narrow line profiles are slightly different for C iv and C iii]. 4. Our analysis suggests a different structure for the C iv and Fe ii+iii emitting regions, with the latter produced in the inner part of the BLR or in a less extended emitting region than C iv.
cm (at 68.3% CI). Similar values are obtained for C iii]. Relative sizes of the carbon-line and V-band continuum emitting-regions are also derived with median values of Rline/Rcont in the range 4 to 29, depending on the FWHM of the line component. 2. The size of the C iv emitting region agrees with the radius-luminosity relationship derived from reverberation mapping. Using the virial theorem, we derive the mass of the black hole in QSO 2237 + 0305 to be MBH ~ 108.3 ± 0.3 M⊙. 3. We find that the C iv and C iii] lines are produced in at least 2 spatially distinct regions, the most compact one giving rise to the broadest component of the line. The broad and narrow line profiles are slightly different for C iv and C iii]. 4. Our analysis suggests a different structure for the C iv and Fe ii+iii emitting regions, with the latter produced in the inner part of the BLR or in a less extended emitting region than C iv.
Key words: gravitational lensing: micro / gravitational lensing: strong / quasars: general / quasars: emission lines / quasars: individual: QSO 2237 + 0305 / line: formation
© ESO, 2011
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


