| Issue |
A&A
Volume 512, March-April 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A16 | |
| Number of page(s) | 9 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200913651 | |
| Published online | 23 March 2010 | |
Soft band X/K luminosity ratios for gas-poor early-type galaxies
1
Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 1,
85741 Garching bei München, Germany e-mail: bogdan@mpa-garching.mpg.de;gilfanov@mpa-garching.mpg.de
2
Space Research Institute, Russian Academy of
Sciences, Profsoyuznaya 84/32, 117997 Moscow, Russia
Received:
12
November
2009
Accepted:
9
December
2009
Aims. We aim to place upper limits on the combined X-ray emission from the population of steady nuclear-burning white dwarfs in galaxies. In the framework of the single-degenerate scenario, these systems, known as supersoft sources, are believed to be likely progenitors of Type Ia supernovae.
Methods. From the Chandra archive, we selected normal early-type galaxies with the point source detection sensitivity better than 1037 erg s-1 in order to minimize the contribution of unresolved low-mass X-ray binaries. The galaxies, contaminated by emission from ionized ISM, were identified based on the analysis of radial surface brightness profiles and energy spectra. The sample was complemented by the bulge of M 31 and the data for the solar neighborhood. To cover a broad range of ages, we also included NGC 3377 and NGC 3585 which represent the young end of the age distribution for elliptical galaxies. Our final sample includes eight gas-poor galaxies for which we determine LX/LK ratios in the 0.3-0.7 keV energy band. This choice of the energy band was optimized to detect soft emission from thermonuclear-burning on the surface of an accreting white dwarf. In computing the LX we included both unresolved emission and soft resolved sources with the color temperature of kTbb ≤ 200 eV.
Results. We find that the X/K luminosity ratios are in a rather narrow range
of (1.7-3.2) × 1027 erg s-1 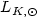 . The
data show no obvious trends with mass, age, or metallicity of the host
galaxy, although a weak anti-correlation with the Galactic NH appears
to exist. It is much flatter than predicted for a blackbody emission
spectrum with temperature of ~ 50-75 eV, suggesting that
sources with such soft spectra contribute significantly less than a
half to the observed X/K ratios. However, the correlation of the
X/K ratios with NH has a significant scatter and in the strict
statistical sense cannot be adequately described by a superposition
of a power law and a blackbody components with reasonable parameters,
thus precluding quantitative constraints on the contribution from soft
sources.
. The
data show no obvious trends with mass, age, or metallicity of the host
galaxy, although a weak anti-correlation with the Galactic NH appears
to exist. It is much flatter than predicted for a blackbody emission
spectrum with temperature of ~ 50-75 eV, suggesting that
sources with such soft spectra contribute significantly less than a
half to the observed X/K ratios. However, the correlation of the
X/K ratios with NH has a significant scatter and in the strict
statistical sense cannot be adequately described by a superposition
of a power law and a blackbody components with reasonable parameters,
thus precluding quantitative constraints on the contribution from soft
sources.
Key words: galaxies: elliptical and lenticular, cD / galaxies: stellar content / X-rays: binaries / X-rays: galaxies / X-rays: ISM
© ESO, 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


