| Issue |
A&A
Volume 509, January 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | L8 | |
| Number of page(s) | 4 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200913583 | |
| Published online | 19 January 2010 | |
Letter to the Editor
The column density towards LMC X-1
1
Dr. Karl Remeis-Observatory & ECAP, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Sternwartstr. 7, 96049 Bamberg, Germany e-mail: Manfred.Hanke@sternwarte.uni-erlangen.de
2
MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, NE80-6077, 77 Mass. Ave., Cambridge, MA 02139, USA
Received:
2
November
2009
Accepted:
17
December
2009
We measure the neutral absorption towards the black hole X-ray binary system LMC X-1 from six archival soft X-ray spectra obtained with the gratings and/or CCD detectors on Chandra, XMM-Newton, and Swift. Four spectral models for the soft continuum are investigated. While the powerlaw model may overestimate 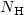 considerably, the others give consistent results. Taking the lower metalicity of the Large Magellanic Cloud into account, we find equivalent hydrogen column densities of
considerably, the others give consistent results. Taking the lower metalicity of the Large Magellanic Cloud into account, we find equivalent hydrogen column densities of 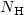 = (1.0-1.3)
= (1.0-1.3)  1022 cm-2, with a systematic dependence on the orbital phase. This variation in the neutral absorption can nearly explain the orbital modulation of the soft X-ray flux recently detected with the All Sky Monitor (ASM) on the Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE).
1022 cm-2, with a systematic dependence on the orbital phase. This variation in the neutral absorption can nearly explain the orbital modulation of the soft X-ray flux recently detected with the All Sky Monitor (ASM) on the Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE).
Key words: X-rays: individuals: LMC X-1 / X-rays: binaries / X-rays: ISM / galaxies: abundances
© ESO, 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


