| Issue |
A&A
Volume 507, Number 1, November III 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 53 - 59 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200911998 | |
| Published online | 08 September 2009 | |
Research Note
Probing the cosmographic parameters to distinguish between dark energy and modified gravity models
1
Department of Astronomy, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, PR China e-mail: fayinwang@nju.edu.cn
2
Department of Astronomy, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 78712, USA
3
Purple Mountain Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing 210008, PR China
4
Joint Center for Particle, Nuclear Physics and Cosmology, Nanjing University – Purple Mountain Observatory, Nanjing 210093, PR China
Received:
6
March
2009
Accepted:
4
August
2009
Aims. In this paper we investigate the deceleration, jerk and snap parameters to distinguish between the dark energy and modified gravity models using high redshift gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) and supernovae (SNe).
Methods. We first derive the expressions of deceleration, jerk and snap parameters in dark energy and modified gravity models. In order to constrain the cosmographic parameters, we calibrate the GRB luminosity relations without assuming any cosmological models using SNe Ia. Then we constrain the model parameters (including dark energy and modified gravity models) using type Ia supernovae and gamma-ray bursts. Finally we calculate the cosmographic parameters. GRBs can extend the redshift-distance relation up to high redshifts, because they can be detected to high redshifts.
Results. We find that the statefinder pair 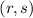 could not be used to distinguish between some dark energy and modified gravity models, but these models could be differentiated by the snap
parameter. Using the model-independent constraints on cosmographic parameters, we conclude that the ΛCDM model is consistent with current data.
could not be used to distinguish between some dark energy and modified gravity models, but these models could be differentiated by the snap
parameter. Using the model-independent constraints on cosmographic parameters, we conclude that the ΛCDM model is consistent with current data.
Key words: gamma rays: bursts / cosmology: cosmological parameters / cosmology: distance scale
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


