| Issue |
A&A
Volume 497, Number 2, April II 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 537 - 543 | |
| Section | The Sun | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200811183 | |
| Published online | 05 March 2009 | |
Time-dependent hydrodynamical simulations of slow solar wind, coronal inflows, and polar plumes
1
Observatoire de Paris, LUTH, CNRS, 92195 Meudon, France e-mail: rui.pinto@obspm.fr
2
Space Science Division, Naval Research Laboratory,Washington, DC 20375-5352, USA e-mail: yi.wang@nrl.navy.mil
Received:
17
October
2008
Accepted:
21
February
2009
Aims. We explore the effects of varying the areal expansion rate and coronal heating function on the solar wind flow.
Methods. We use a one-dimensional, time-dependent hydrodynamical
code. The computational
domain extends from near the photosphere, where nonreflecting
boundary conditions are applied, to 30 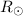 , and includes a
transition region where heat conduction and radiative losses
dominate.
, and includes a
transition region where heat conduction and radiative losses
dominate.
Results. We confirm that the observed inverse relationship between asymptotic wind speed and expansion factor is obtained if the coronal heating rate is a function of the local magnetic field strength. We show that inflows can be generated by suddenly increasing the rate of flux-tube expansion and suggest that this process may be involved in the closing-down of flux at coronal hole boundaries. We also simulate the formation and decay of a polar plume, by including an additional, time-dependent heating source near the base of the flux tube.
Key words: interplanetary medium / solar wind / Sun: corona / Sun: magnetic fields
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


