| Issue |
A&A
Volume 474, Number 2, November I 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 515 - 520 | |
| Section | Galactic structure, stellar clusters, and populations | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078247 | |
| Published online | 28 August 2007 | |
The distance to the Orion Nebula
1
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 53121 Bonn, Germany e-mail: [kmenten;brunthal]@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de
2
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA e-mail: [reid;jforbrich]@cfa.harvard.edu
Received:
9
July
2007
Accepted:
22
August
2007
We have used the Very Long Baseline Array to measure the trigonometric parallax of several member stars of the Orion Nebula Cluster showing non-thermal radio emission. We have determined the distance to the cluster to be 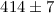 pc. Our distance determination allows for an improved calibration of luminosities and ages of young stars. We have also measured the proper motions of four cluster stars which, when accurate radial velocities are measured, will put strong constraints on the origin of the cluster.
pc. Our distance determination allows for an improved calibration of luminosities and ages of young stars. We have also measured the proper motions of four cluster stars which, when accurate radial velocities are measured, will put strong constraints on the origin of the cluster.
Key words: stars: pre-main sequence / radio continuum: stars / techniques: interferometic / astrometry
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


