| Issue |
A&A
Volume 448, Number 3, March IV 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 843 - 852 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20053409 | |
| Published online | 03 March 2006 | |
Relativistic cross sections of mass stripping and tidal disruption of a star by a super-massive rotating black hole
1
Astro Space Centre, P. N. Lebedev Physical Institute, 4/32 Profsoyuznaya Street, Moscow 117810, Russia e-mail: P.Ivanov@damtp.cam.ac.uk
2
Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge, Centre for Mathematical Sciences, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge CB3 0WA, UK
3
INTEGRAL Science Data Centre, Chemin d'Écogia 16, 1290 Versoix, Switzerland
4
Geneva Observatory, 51 ch. des Maillettes, 1290 Sauverny, Switzerland
Received:
11
May
2005
Accepted:
28
September
2005
Aims.We consider the problem of tidal disruption of
a star by a super-massive rotating black hole.Methods. Using a numerically
fast Lagrangian model of a tidally disrupted star developed
in our previous works,
we survey the parameter space of the
problem and find regions where the total
disruption of the star or a partial mass loss from the star takes
place as a result of fly-by around the black hole.
Our treatment is based on General Relativity, and we consider
a range of black hole masses where the tidal disruption
competes with the relativistic effect of direct capture of
stars by the black hole. We model the star
as a full polytrope with 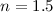 with the solar mass and radius.
We show that our results can also be used to obtain
the amount of mass lost by stars with different
stellar masses and radii.Results.We find that the results can be conveniently represented on
the plane of specific orbital angular momenta of the star
with the solar mass and radius.
We show that our results can also be used to obtain
the amount of mass lost by stars with different
stellar masses and radii.Results.We find that the results can be conveniently represented on
the plane of specific orbital angular momenta of the star
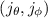 . We calculate the contours of
a given mass loss of the star on this plane,
for a given black hole mass M, rotational parameter a and inclination of the trajectory of the star with respect to the
black hole equatorial plane. In the following such contours are
referred to as the tidal cross sections.
It is shown that the tidal cross sections can be approximated as
circles symmetric above the axis
. We calculate the contours of
a given mass loss of the star on this plane,
for a given black hole mass M, rotational parameter a and inclination of the trajectory of the star with respect to the
black hole equatorial plane. In the following such contours are
referred to as the tidal cross sections.
It is shown that the tidal cross sections can be approximated as
circles symmetric above the axis 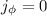 , and
shifted with respect to the origin of the coordinates in the
direction of negative
, and
shifted with respect to the origin of the coordinates in the
direction of negative 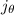 . The radii and shifts of these
circles are obtained numerically for the black hole masses in the
range
. The radii and shifts of these
circles are obtained numerically for the black hole masses in the
range 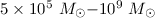 and different values of a. It is shown that when
and different values of a. It is shown that when 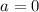 tidal disruption takes place for
tidal disruption takes place for
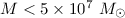 and when
and when 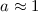 tidal disruption is possible for
tidal disruption is possible for 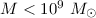 .
.
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


