| Issue |
A&A
Volume 425, Number 3, October III 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 899 - 911 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:200400025 | |
| Published online | 28 September 2004 | |
Volume filling factors of the ISM phases in star forming galaxies
I. The role of the disk-halo interaction
1
Department of Mathematics, University of Évora, R. Romão Ramalho 59, 7000 Évora, Portugal e-mail: mavillez@galaxy.lca.uevora.pt
2
Max-Planck-Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstraße, Postfach 1312, 85741 Garching, Germany e-mail: breitsch@mpe.mpg.de
3
Present address: Institut für Astronomie, Universität Wien, Türkenschanzstr. 17, 1180 Wien, Austria e-mail: breitschwerdt@astro.univie.ac.at
Received:
10
July
2003
Accepted:
23
June
2004
The role of matter circulation between the disk and
halo in establishing the volume filling factors of the different
ISM phases in the Galactic disk (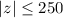 pc) is
investigated, using a modified version of the three-dimensional
supernova-driven ISM model of Avillez ([CITE]). We carried out
adaptive mesh refinement simulations of the ISM with five supernova
rates (in units of the Galactic value),
pc) is
investigated, using a modified version of the three-dimensional
supernova-driven ISM model of Avillez ([CITE]). We carried out
adaptive mesh refinement simulations of the ISM with five supernova
rates (in units of the Galactic value), 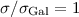 , 2,
4, 8 and 16 (corresponding to starburst conditions) using three
finer level resolutions of 2.5, 1.25 and 0.625 pc, allowing us to
understand how resolution would affect the volumes of gas phases in
pressure equilibrium. We find that the volume filling factors of
the different ISM phases depend sensitively on the existence of a
duty cycle between the disk and halo acting as a pressure release
valve for the hot (
, 2,
4, 8 and 16 (corresponding to starburst conditions) using three
finer level resolutions of 2.5, 1.25 and 0.625 pc, allowing us to
understand how resolution would affect the volumes of gas phases in
pressure equilibrium. We find that the volume filling factors of
the different ISM phases depend sensitively on the existence of a
duty cycle between the disk and halo acting as a pressure release
valve for the hot ( K) phase in the disk. The amount
of cold gas (defined as the gas with
K) phase in the disk. The amount
of cold gas (defined as the gas with  K) picked up in the
simulations varies from a value of 19% for
K) picked up in the
simulations varies from a value of 19% for 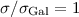 to
to 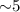 % for
% for  and
and 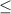 1% for higher
SN rates. Background heating prevents the cold gas from immediate
collapse and thus ensures the stability of the cold gas phase. The
mean occupation fraction of the hot phase varies from about 17%
for the Galactic SN rate to ∼28%, for
1% for higher
SN rates. Background heating prevents the cold gas from immediate
collapse and thus ensures the stability of the cold gas phase. The
mean occupation fraction of the hot phase varies from about 17%
for the Galactic SN rate to ∼28%, for
 , and to
, and to 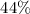 for
for
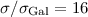 . Overall the filling factor of the
hot gas does not increase much as we move towards higher SN rates,
following a power law of
. Overall the filling factor of the
hot gas does not increase much as we move towards higher SN rates,
following a power law of 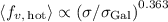 . Such a modest dependence
on the SN rate is a consequence of the evacuation of the hot phase
into the halo through the duty cycle. This leads to volume filling
factors of the hot phase considerably smaller than those predicted
in the three-phase model of McKee & Ostriker ([CITE]) even in the
absence of magnetic fields.
. Such a modest dependence
on the SN rate is a consequence of the evacuation of the hot phase
into the halo through the duty cycle. This leads to volume filling
factors of the hot phase considerably smaller than those predicted
in the three-phase model of McKee & Ostriker ([CITE]) even in the
absence of magnetic fields.
Key words: galaxies: ISM / galaxies: kinematics and dynamics / ISM: structure
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


