| Issue |
A&A
Volume 414, Number 1, January IV 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 69 - 78 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20034113 | |
| Published online | 12 January 2004 | |
The Small Magellanic Cloud in the far infrared*
II. Global properties
1
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany
2
Helsinki University Observatory, Tähtitorninmäki, PO Box 14, 0014 University of Helsinki, Finland
Corresponding author: U. Klaas, klaas@mpia.de
Received:
24
July
2003
Accepted:
7
October
2003
We present global IR properties of the Small Magellanic Cloud
using an ISOPHOT 170 μm map and re-visited IRAS data. The integrated
170 μm flux is 14 950 ± 2300 Jy, and the integrated IR flux is
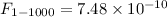 W m-2. Discrete sources
contribute 28%, 29%, and 36% to the integrated flux at 60 μm,
100 μm, and 170 μm, respectively. Most of the total emission
arises from diffuse emission regions surrounding the HII regions. The SED can be modelled by the composition of a 45 K, a 20.5 K and a 10 K
blackbody component with emissivity index
W m-2. Discrete sources
contribute 28%, 29%, and 36% to the integrated flux at 60 μm,
100 μm, and 170 μm, respectively. Most of the total emission
arises from diffuse emission regions surrounding the HII regions. The SED can be modelled by the composition of a 45 K, a 20.5 K and a 10 K
blackbody component with emissivity index 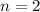 . A color
temperature map is constructed from the ISOPHOT 170 μm and the IRAS 100 μm HiRes maps. The average dust temperature is
. A color
temperature map is constructed from the ISOPHOT 170 μm and the IRAS 100 μm HiRes maps. The average dust temperature is 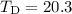 K. The
total dust mass is found to be
K. The
total dust mass is found to be 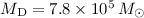 , yielding a gas-to-dust mass ratio
Mgas/
, yielding a gas-to-dust mass ratio
Mgas/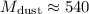 , a value 25 times lower than
found by former studies. The global star formation rate is estimated to
SFR
, a value 25 times lower than
found by former studies. The global star formation rate is estimated to
SFR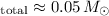 yr-1. The
comparison with other irregular galaxies reveals the SMC as quiet with
no peculiar FIR properties.
yr-1. The
comparison with other irregular galaxies reveals the SMC as quiet with
no peculiar FIR properties.
Key words: galaxies: Magellanic Clouds / ISM: general / ISM: dust, extinction
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


