| Issue |
A&A
Volume 423, Number 2, August IV 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 567 - 577 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20035918 | |
| Published online | 06 August 2004 | |
Multi-wavelength analysis of the dust emission in the Small Magellanic Cloud*
1
UMR 7550, Centre de Données Astronomiques de Strasbourg (CDS), Université Louis Pasteur, 67000 Strasbourg, France e-mail: bot@astro.u-strasbg.fr
2
Institut d'Astrophysique Spatiale, Université Paris-Sud, 91405 Orsay, France
3
UMS 2201, Observatoire de Paris, 75014 Paris, France
Received:
19
December
2003
Accepted:
28
April
2004
We present an analysis of dust grain emission in the diffuse interstellar medium of the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC).
This study is motivated by the availability of 170 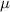 m ISOPHOT data covering a large part of the SMC, with a resolution making it possible to disentangle the diffuse medium from the star forming regions.
After data reduction and subtraction of Galactic foreground emission, we used the ISOPHOT data together with HiRes IRAS data and ATCA/Parkes combined
m ISOPHOT data covering a large part of the SMC, with a resolution making it possible to disentangle the diffuse medium from the star forming regions.
After data reduction and subtraction of Galactic foreground emission, we used the ISOPHOT data together with HiRes IRAS data and ATCA/Parkes combined 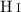 column density maps to determine dust properties for the diffuse medium.
We found a far infrared emissivity per hydrogen atom 30 times lower than the Solar neighborhood value. The modeling of the spectral energy distribution of the dust, taking into account the enhanced interstellar radiation field, gives a similar conclusion for the smallest grains (PAHs and very small grains) emitting at shorter wavelength. Assuming Galactic dust composition in the SMC, this result implies a difference in the gas-to-dust ratio (GDR) 3 times larger than the difference in metallicity.
This low depletion of heavy elements in dust could be specific of the diffuse ISM and not apply to all the SMC dust if it results from efficient destruction of dust by supernovae explosions.
column density maps to determine dust properties for the diffuse medium.
We found a far infrared emissivity per hydrogen atom 30 times lower than the Solar neighborhood value. The modeling of the spectral energy distribution of the dust, taking into account the enhanced interstellar radiation field, gives a similar conclusion for the smallest grains (PAHs and very small grains) emitting at shorter wavelength. Assuming Galactic dust composition in the SMC, this result implies a difference in the gas-to-dust ratio (GDR) 3 times larger than the difference in metallicity.
This low depletion of heavy elements in dust could be specific of the diffuse ISM and not apply to all the SMC dust if it results from efficient destruction of dust by supernovae explosions.
Key words: ISM: dust, extinction / galaxies: Magellanic Clouds / ISM: abundances / ISM: evolution / galaxies: ISM
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


