| Issue |
A&A
Volume 405, Number 3, July III 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 975 - 980 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20030718 | |
| Published online | 30 June 2003 | |
High-z nebulae: Ionization by stars or by an obscured QSO?
1
Instituto de Astronomía, UNAM, Ap. 70-264, 04510 DF, México e-mail: binette@astroscu.unam.mx
2
Mt. Stromlo Observatory, Cotter Rd., Weston Creek, ACT 2611, USA e-mail: bgroves@mso.anu.edu.au
3
Dept. of Natural Sciences, Univ. of Hertfordshire, College Lane, Hatfield, Herts AL10 9AB, UK
4
ST-ECF, Karl Schwarzschild Str. 2, 85748 Garching-bei-München, Germany e-mail: rfosbury@eso.org
5
Dept. of Physics, Rochester Institute of Technology, 85 Lomb Memorial Dr., Rochester, NY 14623-5603, USA
Corresponding author: B; Groves, bgroves@mso.anu.edu.au
Received:
19
November
2002
Accepted:
8
May
2003
The gravitational arc
observed by Holden et al. at 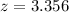 reveals strong emission lines of ,
, but no . The lines were
modelled assuming photoionization by a thermal distribution hotter
than 60 000 K. This paper considers an alternative ionizing source
consisting of a partially absorbed powerlaw. We compare the line
ratios from a low metallicity nebula (
reveals strong emission lines of ,
, but no . The lines were
modelled assuming photoionization by a thermal distribution hotter
than 60 000 K. This paper considers an alternative ionizing source
consisting of a partially absorbed powerlaw. We compare the line
ratios from a low metallicity nebula (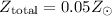 )
photoionized by such filtered continuum with those produced by a
zero-metallicity star of
)
photoionized by such filtered continuum with those produced by a
zero-metallicity star of 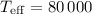 K. We find that the
latter generally produces stronger emission lines of C, N and O than
the absorbed powerlaw, even when their respective /Hβ ratio is
matched. The absorbed powerlaw generates ,
and nebular lines weaker than the canonical direct
powerlaw, although at a much higher level than the 80 000 K
stellar atmosphere. As a result of the large partially ionized zone
created by the absorbed powerlaw, the optical and
lines and the and lines in the UV are much
stronger than in the stellar case. These constitute the best
discriminant for differentiating the predictions of the absorbed case
from those of the stellar model.
K. We find that the
latter generally produces stronger emission lines of C, N and O than
the absorbed powerlaw, even when their respective /Hβ ratio is
matched. The absorbed powerlaw generates ,
and nebular lines weaker than the canonical direct
powerlaw, although at a much higher level than the 80 000 K
stellar atmosphere. As a result of the large partially ionized zone
created by the absorbed powerlaw, the optical and
lines and the and lines in the UV are much
stronger than in the stellar case. These constitute the best
discriminant for differentiating the predictions of the absorbed case
from those of the stellar model.
Key words: line: formation / quasars: emission lines / galaxies: formation / cosmology: early Universe
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


