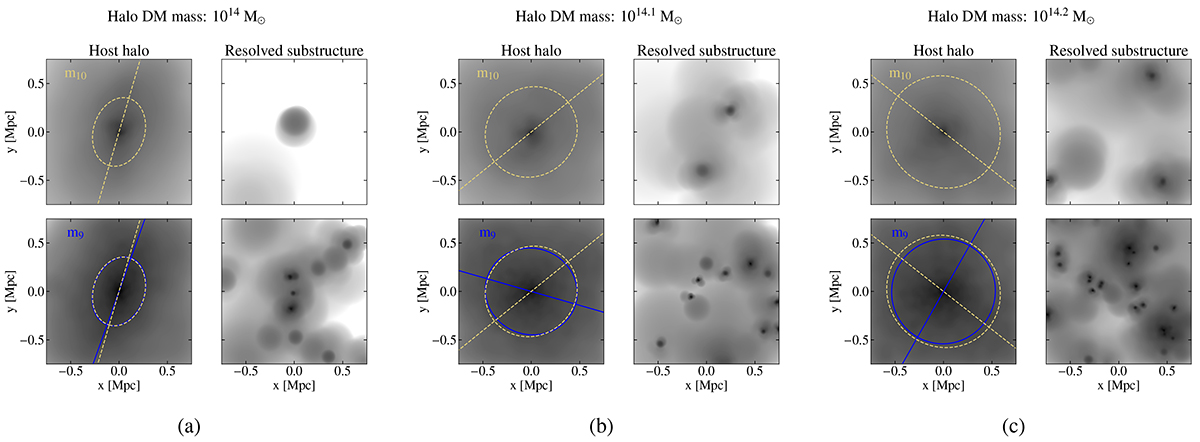
Fig. B.2.
Download original image
Examples of matched haloes in the m10 run (upper row) and the m9 run (bottom row). The left panels of figures (a), (b) and (c) show the host halo with the projected ellipse and orientation angle over plotted, with the right panels showing the resolved substructures that are excised from the host halo before calculating the inertia tensor. This sources an additional scatter over that from sampling noise. (a) shows an example for which the effect is relatively small, causing a misalignment of only a few degrees. (b) is an example of a more spherical halo that is hence more sensitive to the removal of low mass substructures. (c) is another spherical halo for which the orientation angle of the m9 run is almost orthogonal to that from the m10 run.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


