Table 1.
Measurements of ℜ⋆ in nearby environments and simulations.
| System | [i] ℜ⋆ [kpc] (Rvir) | [ii] ℜ⋆ [kpc](Rvir) |
|---|---|---|
| Fornax cluster | 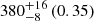 |
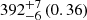 |
| Virgo cluster (A) | 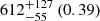 |
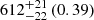 |
| Milky way | 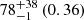 |
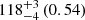 |
| Andromeda (M31) | 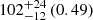 |
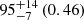 |
| Fornax-type (TNG50) (2D) | 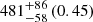 |
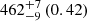 |
| Fornax-type (TNG50) (3D) | 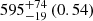 |
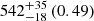 |
| Virgo-type (TNG100) (2D) | 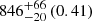 |
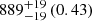 |
| Virgo-type (TNG100) (3D) | 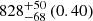 |
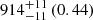 |
| Virgo-type (EAGLE) (2D) | 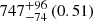 |
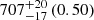 |
| Virgo-type (EAGLE) (3D) | 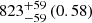 |
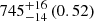 |
Notes. The adopted virial radii for each system are: Fornax 1075 kpc (Schuberth et al. 2010), Virgo A 1550 kpc (McLaughlin 1999), M31 207 kpc (Tamm et al. 2012), MW 216 kpc (Bland-Hawthorn & Gerhard 2016; Shen et al. 2022), Fornax-type TNG50 cluster 1115 kpc, Virgo-type cluster TNG100 2079 kpc, and Virgo-type cluster EAGLE 1442 kpc.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


