Table 7
CEERS z > 0.1 photometric redshift performance metrics.
| Template | Δbias,z>0.1 | σnmad,z>0.1 | ηf,z>0.1 | ηc,z>0.1 | sz>0.1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| A22 | −0.6 ± 0.4 | 50 ± 1 | 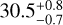 |
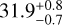 |
98.6 ± 0.1 |
| BlSFH | −6.3 ± 0.5 | 45 ± 1 | 31 ± 1 | 32 ± 1 | 98.7 ± 0.1 |
| CaSFH | −9.2 ± 0.5 | 45 ± 1 | 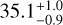 |
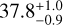 |
97.4 ± 0.1 |
| Ev3 | −6.1 ± 0.5 | 43.8 ± 0.8 | 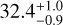 |
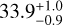 |
98.5 ± 0.1 |
| L23 | −7.0 ± 0.6 | 51 ± 1 | 36 ± 1 | 38 ± 1 | 98.3 ± 0.2 |
| T22 | 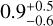 |
50.1 ± 0.9 | 32 ± 1 | 33 ± 1 | 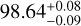 |
| TwSPS | −20.6 ± 0.8 | 54 ± 1 | 45 ± 1 | 52 ± 1 | 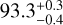 |
Notes. Overview of template performance on the all-redshift (zspec > 0.1) CEERS sample. Specific metrics are defined above (Sect. 3.1). CEERS, being a lower depth survey, offers relatively low accuracy and precision when determining object redshift, and thus a high-redshift sample derived from it will have a lower purity. However, with the large and less costly nature of the survey, astrometric use cases could be employed, with A22 exhibiting the lowest bias of all measurements. The sets T22 and S23 are not included in this analysis because they require pre-selection of high-redshift candidates.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


