Fig. 2
Download original image
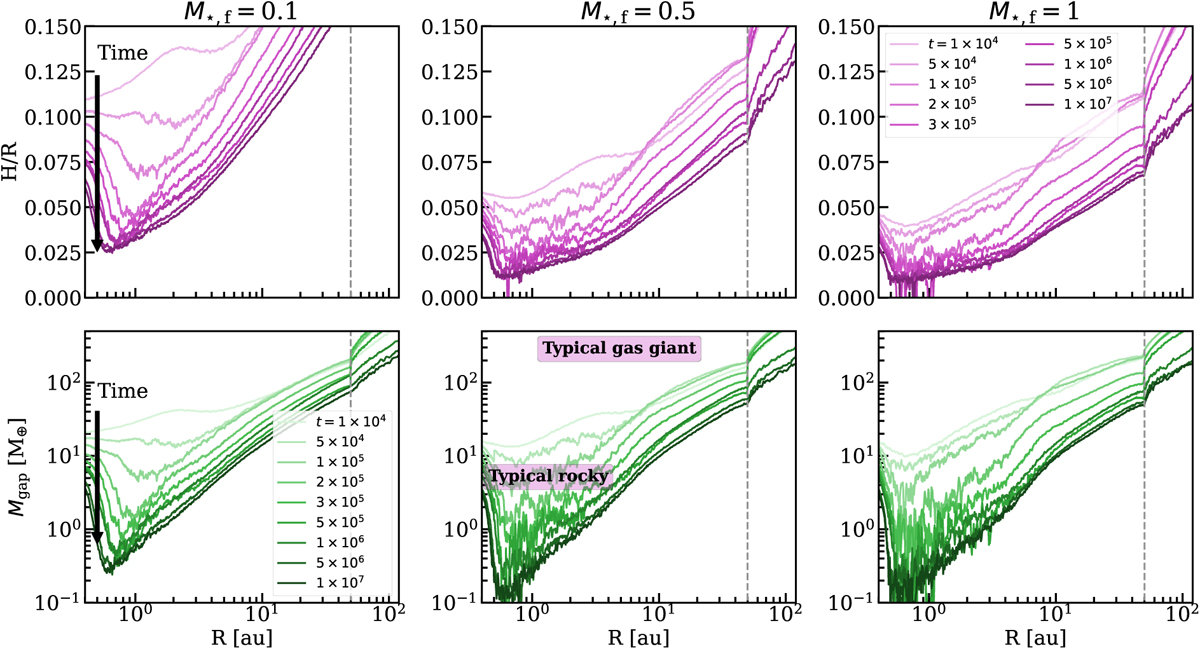
Evolution of disk aspect ratio (top) and minimum planet mass required to open a gap (bottom) from young class 0 disks (lighter colors) to mature class II disks (darker colors) for different final protostellar masses. These models are those with small dust grains (0.1 μ m). The dashed gray line presents the radius of the disk assumed in these models. The typical masses of giant and rocky planets are taken from Zhu & Dong (2021) (also see Akeson et al. 2013). Up to ∼50 M⊕ of a giant planet and an entire rocky planet would create no sign of a dust gap if formed in the protostellar phase (t < 2 × 105 yr).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


