Fig. 3
Download original image
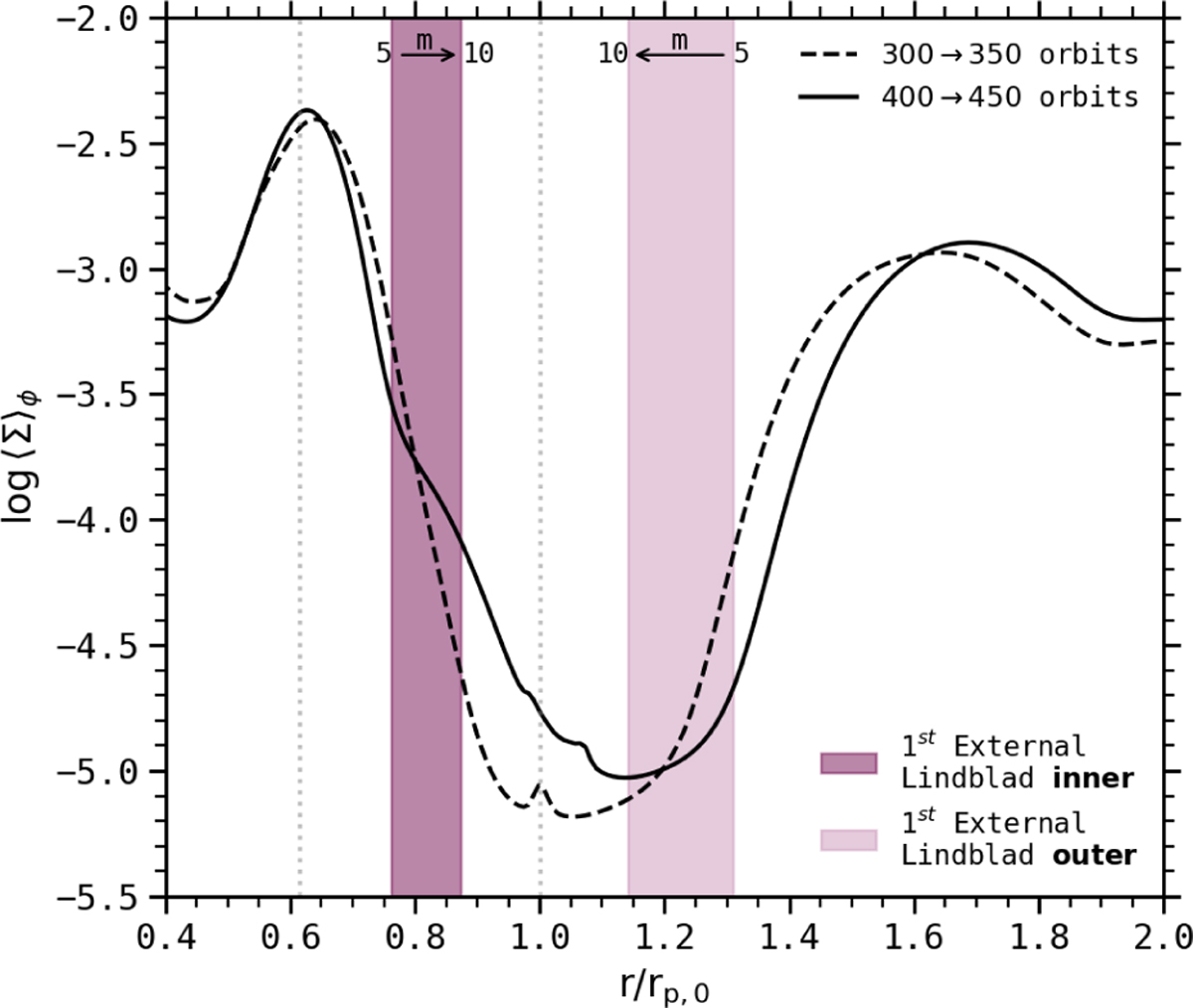
Azimuthal average of the logarithm of the gas surface density ∑ for the run ℳ300 , temporally averaged during a phase of quasi-circular and outward migration (dashed line), and during a phase of stalled and eccentric migration (solid line). The two vertical gray dotted lines show the reconstructed radii where the main sources of high-frequency ΓLi variability are expected to originate from. The purple areas indicate the location of the inner and outer first-order external Lindblad resonances, for the modes m = 5 to m = 10. For the quasi-circular case (dashed line), the wind has already affected the planet gap, with a wider outer gap compared to the inner gap. For the eccentric case (solid line), the gap is globally denser due to the increase of the planet eccentricity. The wind has strongly enhanced the inner gap compared to the outer gap that is even further away from the planet location. The negative density gradient at the planet location could boost a negative corotation torque.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


