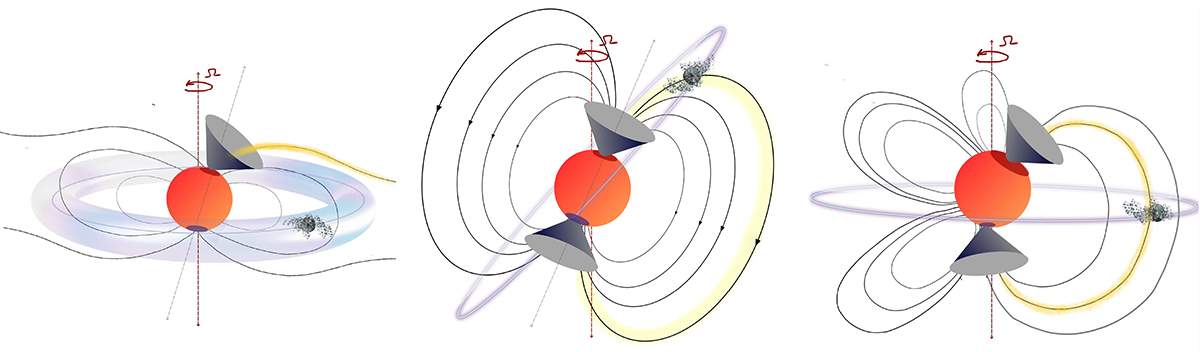
Fig. D.1.
Download original image
Illustrations of possible scenarios that could trigger the beamed radio ECM emission along a wide cone. The yellow lines qualitatively mark the flux tubes at the footprints from which ECM emits radio-beamed emission, marked by the gray cones. In all cases, the orbit of the occulting material is seen nearly edge-on by the observer, which explains the optical dips. Left: Non-Io decametric-like emission, for which the occulting object might be only an indirect source of plasma. Center: Approximately corotating, evaporating planet causing optical dips, with a very inclined orbit. Right: Same as the center, but for a complex, multipolar stellar magnetic field planetary orbit orthogonal to the stellar rotation axis.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


