Fig. 2.
Download original image
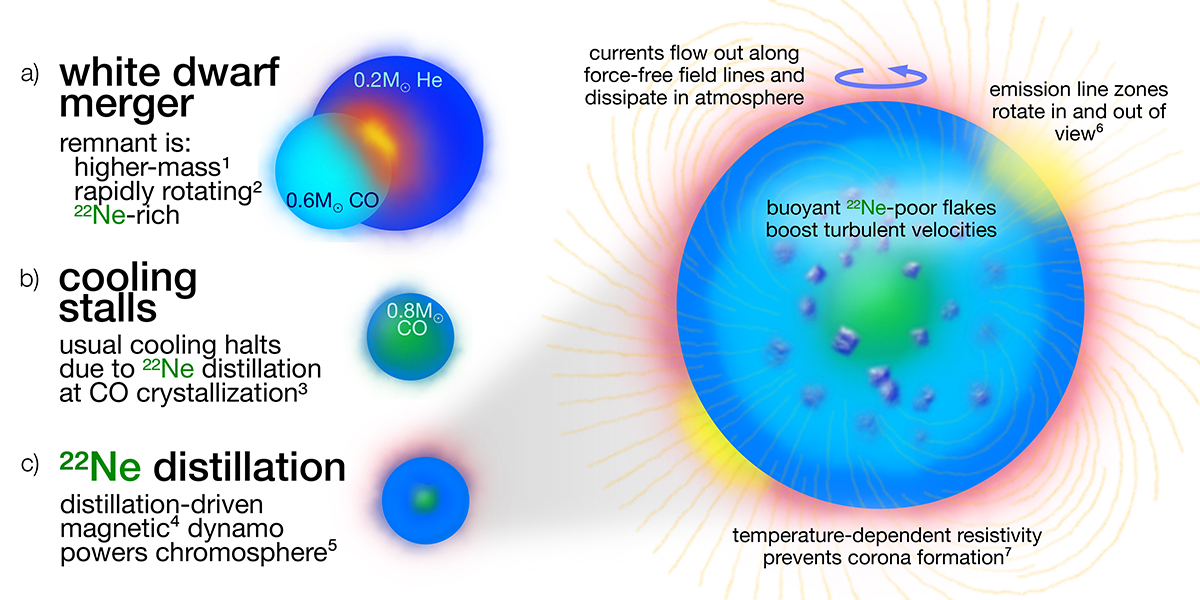
Illustrative summary of the model advanced in this work. (a) DAHe white dwarf created by a stellar merger, such as between a carbon–oxygen and helium-core white dwarf (as shown by, e.g. Clayton et al. 2007; Menon et al. 2013) or subgiant. (b) Resulting 22Ne-rich remnant cools until the onset of carbon–oxygen crystallization and 22Ne distillation, which halt the cooling near Teff ≈ 7500 K. (c) Distillation also provides sufficient energy to sustain a strong magnetic dynamo that powers the characteristic chromospheric emission through Ohmic heating. Superscript numbers indicate observed properties of DAHe stars: 1typical masses M ≃ 0.8 M⊙, 2rapid rotation, 3similar Teff ≈ 7500 K near that of carbon–oxygen crystallization, 4magnetic fields B ≳ 5 MG, 5Balmer lines in emission, 6rotational light curve modulation, and 7lack of coronal emission in the prototype.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


