Fig. 11.
Download original image
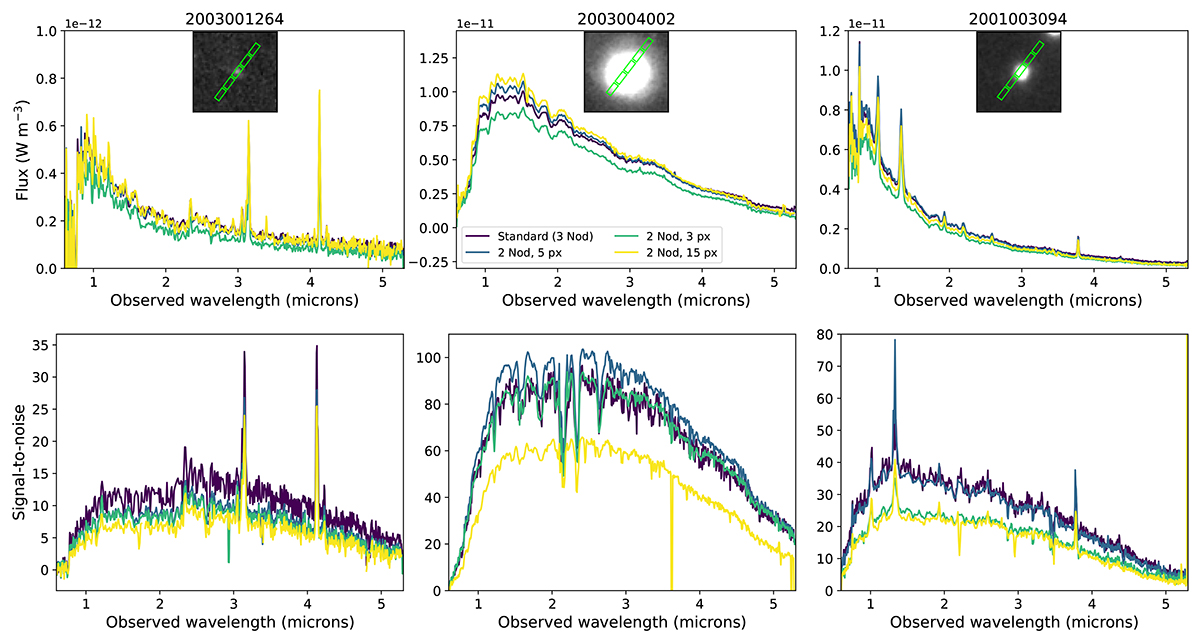
Example Wide PRISM spectra (top) and signal-to-noise (bottom) for three objects in GOODS-N, showing the effect of the choice of the nodding pattern and extraction on the resulting 1D spectra. Insets show the HST/WFC3 F160W images with the NIRSpec MSA shutters overplotted; note a 1 × 3 microshutter configuration with the observed three-point nodding in the PRISM results in a projected area of 1 × 5 shutters on the sky. Left: A compact object, well-centered in the MSA: there is very little difference between the different nodding and extraction choices. Center: A very extended object: in this case, self-subtraction becomes an issue with the three-point nodding resulting in a higher signal and signal-to-noise when the two-point reduction is used. Right: An intermediate case: the choice of different extractions can be motivated scientifically (see e.g. Section 5.8).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


