Fig. 6
Download original image
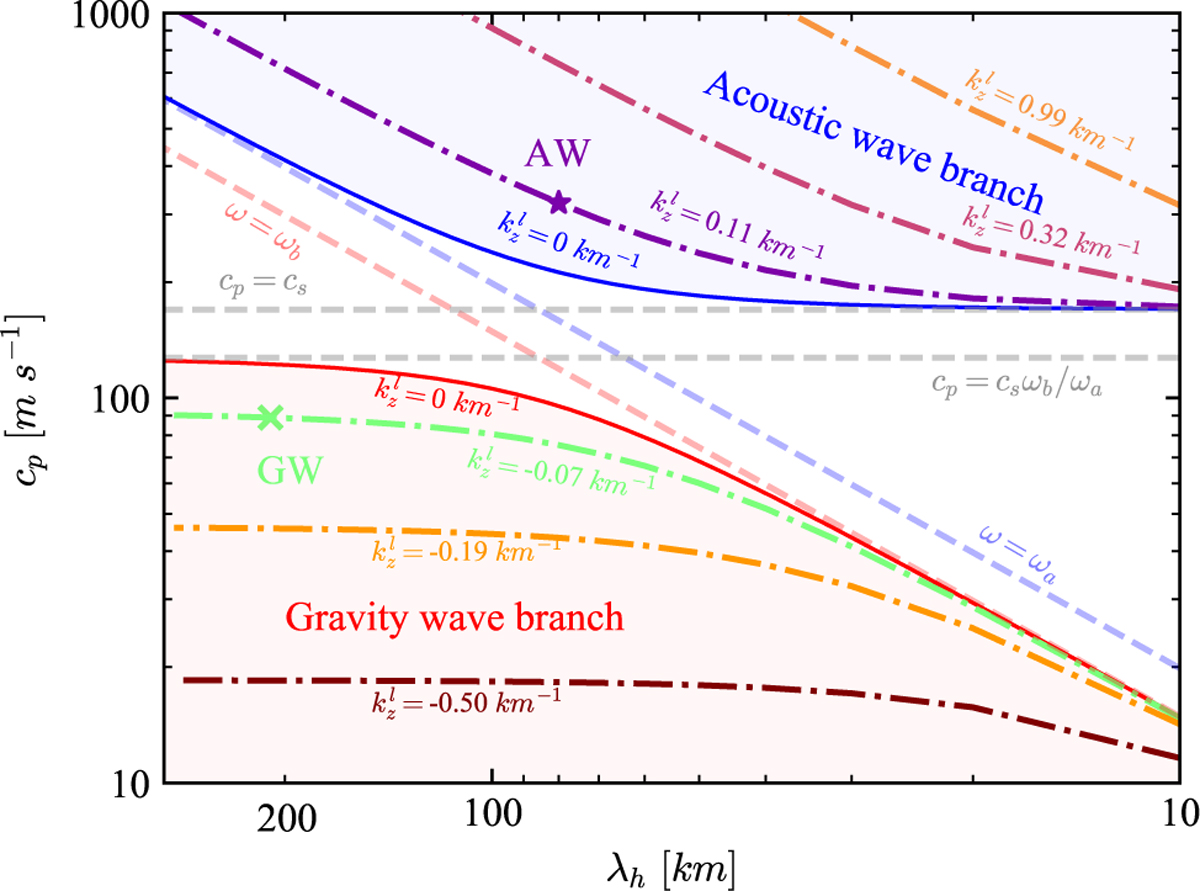
λh, − cp parameter space of acoustic-gravity waves. λh is the horizontal wavelength and cp is the horizontal phase speed. For the acoustic wave branch, ω > ωa and cp > cs, where ω and cs refer to the wave frequency and local sound speed, respectively. For the gravity wave branch, ω < ωb and cp < csωb/ωa. Here ωa and ωb, represent the acoustic cutoff and Brunt-Väisälä frequency, respectively. The two wave branches are bounded by two solid curves along which the vertical wavenum-ber ![]() is equal to zero. To compare the model result with spacecraft observation, three wave sets for each acoustic and gravity wave branch are selected, whose
is equal to zero. To compare the model result with spacecraft observation, three wave sets for each acoustic and gravity wave branch are selected, whose ![]() are 0.11, 0.32, and 0.99 km−1 and −0.07, −0.19, and −0.5 km−1, respectively. Two characteristic wave modes named by “AW” and “GW” and marked by “★” and “×", respectively, are selected to examine the impact of acoustic-gravity waves on the ionosphere. The period, horizontal wavelength, and phase speed are 4.2 min, 80 km, and 321 m s−1 for “AW” and 39.4 min, 210 km, and 89 m s−1 for “GW”.
are 0.11, 0.32, and 0.99 km−1 and −0.07, −0.19, and −0.5 km−1, respectively. Two characteristic wave modes named by “AW” and “GW” and marked by “★” and “×", respectively, are selected to examine the impact of acoustic-gravity waves on the ionosphere. The period, horizontal wavelength, and phase speed are 4.2 min, 80 km, and 321 m s−1 for “AW” and 39.4 min, 210 km, and 89 m s−1 for “GW”.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


