Fig. 4
Download original image
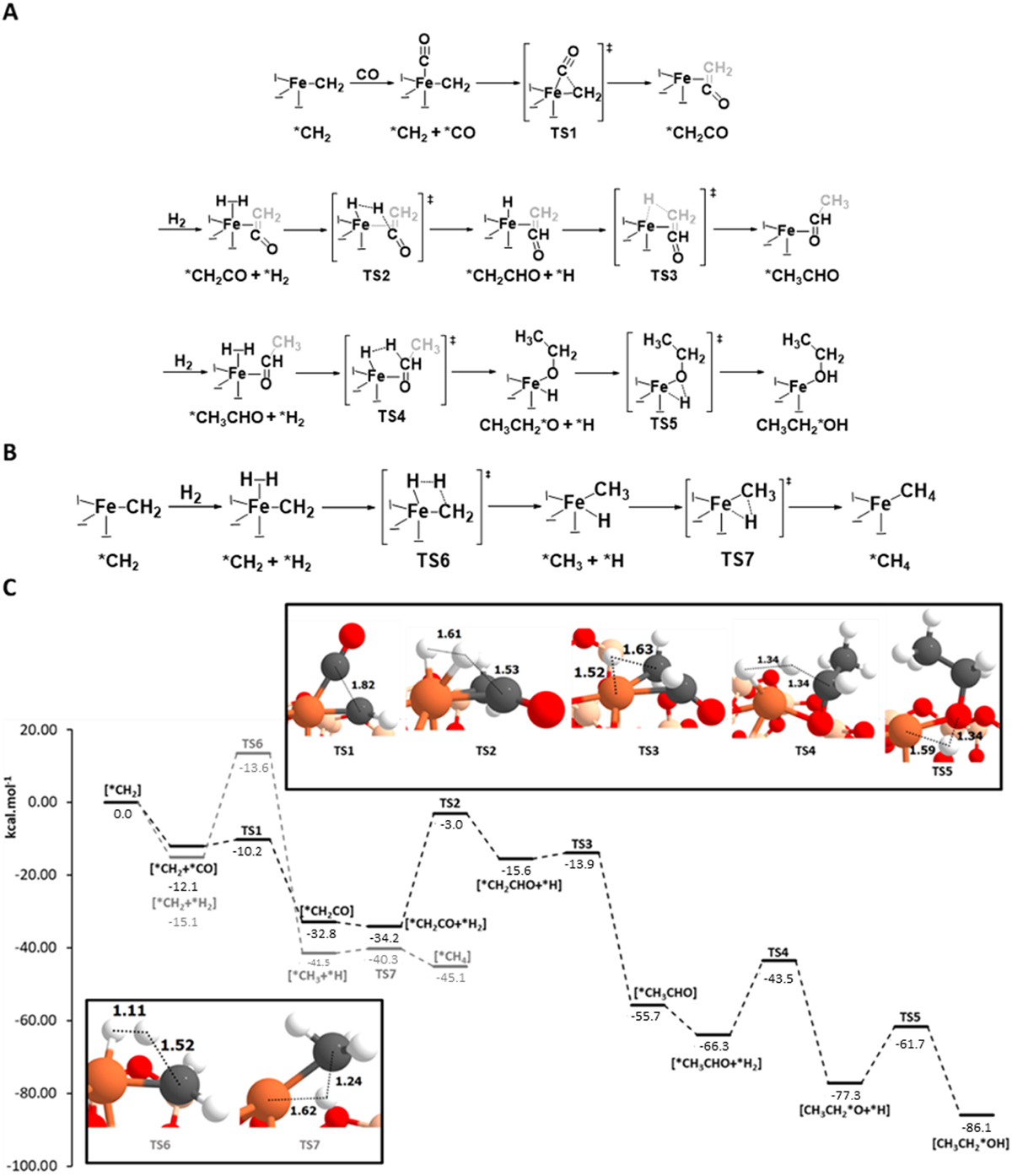
(A) Reaction mechanism for the ethanol formation from the direct CH2 – CO coupling forming CH2 and O, the reaction of CH2 with an incoming CO, forming H2CCO, and subsequent hydrogenations. (B) Reaction mechanism for the methane formation from hydrogenation of CH2. (C) ZPE-corrected PESs (in kcal mol–1 ) for the ethanol formation (black) and methane formation (gray) mechanisms, using as the 0th reference energy the Fe0@SiO2-CH2 + H2 + CO asymptote. The optimized geometries of all the transition state structures (bond distances in Å) are also shown. The asterisk symbol (*) denotes from which atom the relevant molecule is coordinated with Fe. Color-coding: H atoms are represented in white, C atoms in gray, O atoms in red, Si atoms in beige, and Fe atoms in orange.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


