Fig. 4.
Download original image
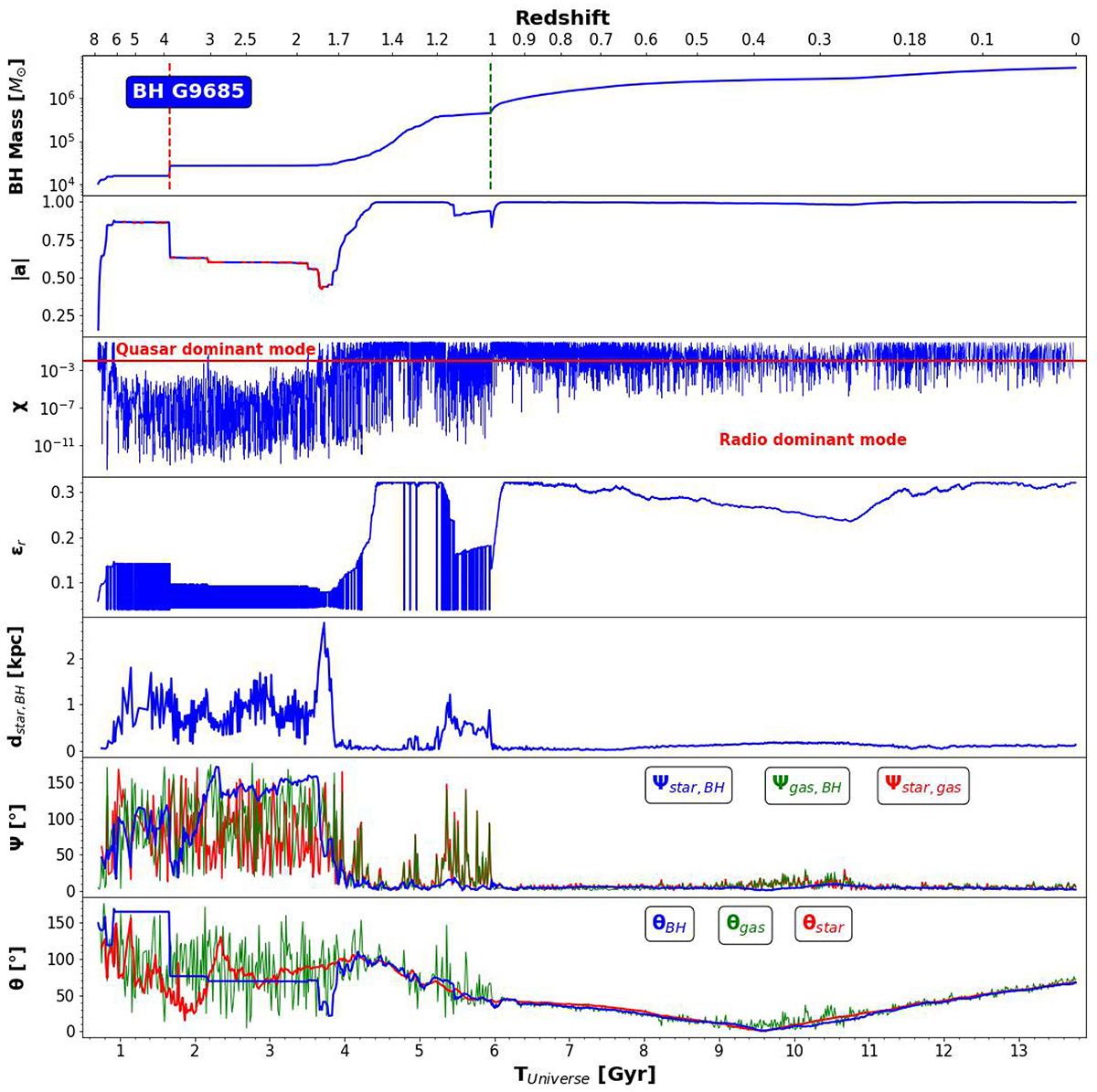
Evolution of relevant properties of the central black hole in the GALACTICA run G9685. From top to bottom: (1) BH mass evolution. The red and green dashed lines indicate epochs of major and minor mergers episodes respectively; (2) BH spin evolution |a|. Red colors indicates when the gas accretion disk is in counter-rotation (i.e., a < 0); (3) the Eddington ratio evolution (χ). The red line delimits the quasar dominant mode (χ > 0.01) and the radio dominant mode (χ < 0.01); (4) the evolution of the radiative efficiency of the gas accretion disk (ϵr); (5) the variation of the distance separation between the location of the BH and the center of its host galaxy (dstar, BH); (6) the evolution of the angle Ψstar, BH between the BH spin and the angular momentum of the stellar component (blue) estimated within one effective radius. We also plot the angle between the BH spin and the angular momentum of the gas accretion disk (green) as well as the angle between the stellar and the accreted gas component (red); (7) the evolution of the polar angle θ describing the orientation of the BH spin (blue), the stellar (red) and gas accretion disk (green) angular momenta relative to a fixed reference frame of the simulation. The fraction of mass gained through BH mergers is fBH, merger = 1.53%. The cosmic evolution of Ψstar, BH follows three different regimes.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


