Fig. 5
Download original image
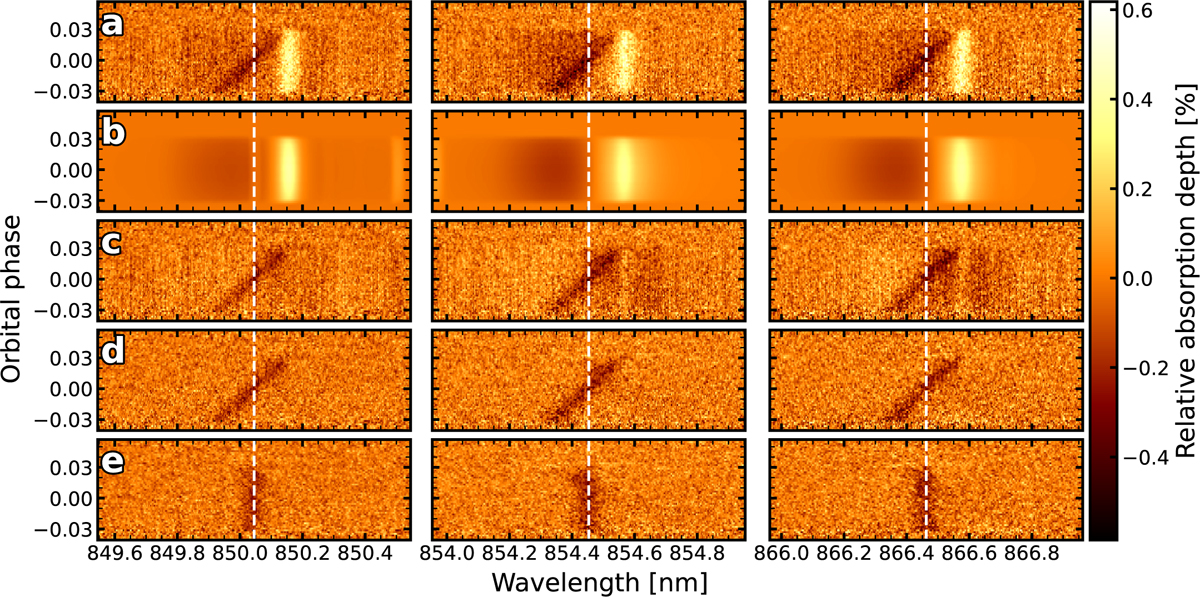
Analysis steps shown for the Ca+ infrared triplet. a: combined transmission spectra of both time series in the rest frame of the star. The dark absorption feature is the planetary atmosphere. The bright emission-like feature is the residual originating from the spectra behind the planet during transit (Rossiter–McLaughlin effect). b: best fit for the stellar residual using the parameters in Table 3. c: combined transmission spectrum after dividing out the best fit for the stellar residual. d: panel c after correcting for systematic noise in the rest frame of the star (vertical de-trending). e: same as panel d, but in the rest frame of the planet. The vertical absorption features are the Ca+ lines of the planetary atmosphere.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


