Fig. 3.
Download original image
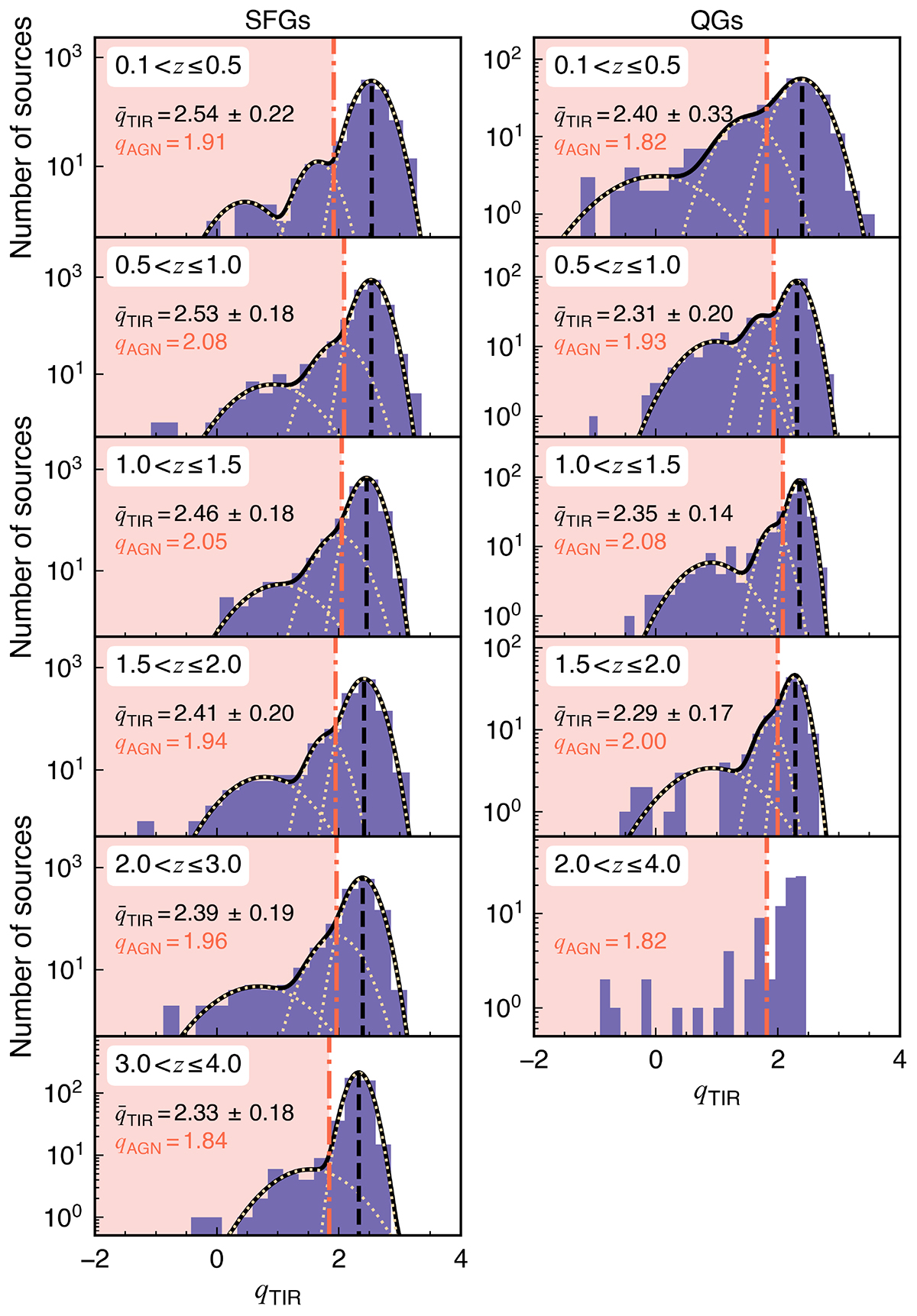
Distribution of IR-radio-ratio (qTIR) in SFGs (left column) and QGs (right column) at different redshift bins. The qTIR distributions were obtained by merging the Radio Sources Sample from the GOODS-N and COSMOS/UltraVISTA fields. Each yellow dotted curve represents a single-Gaussian model, while the black solid curve represents the best-fit model to the entire qTIR distribution. The vertical black dashed line (corresponding to the ![]() value in the figure) represents the peak position of the highest Gaussian component. The vertical red dash-dotted line (corresponding to the qAGN value in the figure) represents the cross point between the highest Gaussian component and the second-highest Gaussian component, which is used as the threshold to separate SFGs and radio-excess AGNs in this work. For QGs at 2.0 < z ≤ 4.0, it is difficult to find a best-fit model due to the low source number, so here the threshold at 0.1 < z ≤ 0.5 was used, which does not have a significant effect on the results.
value in the figure) represents the peak position of the highest Gaussian component. The vertical red dash-dotted line (corresponding to the qAGN value in the figure) represents the cross point between the highest Gaussian component and the second-highest Gaussian component, which is used as the threshold to separate SFGs and radio-excess AGNs in this work. For QGs at 2.0 < z ≤ 4.0, it is difficult to find a best-fit model due to the low source number, so here the threshold at 0.1 < z ≤ 0.5 was used, which does not have a significant effect on the results.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


