Fig. 14.
Download original image
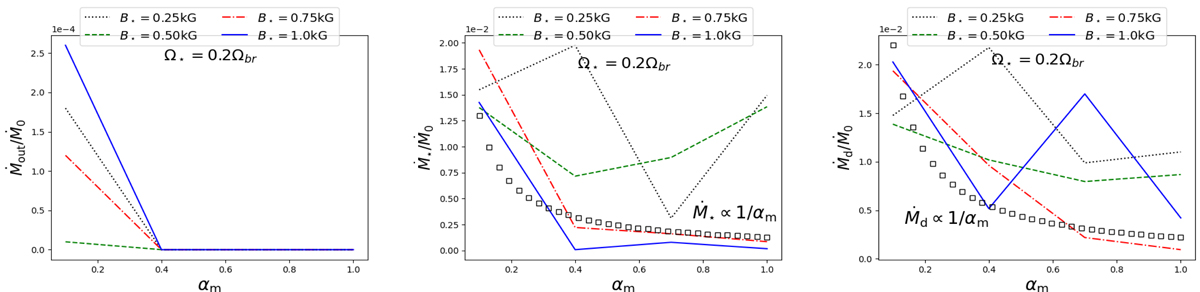
Components of the mass fluxes, Ṁ, in terms of the dependence of the anomalous resistive coefficient, αm, for different strengths of the stellar magnetic field in the cases with fastest stellar rotation in our simulations, Ω⋆ = 0.2Ωbr. The values of Ṁout and Ṁd are both computed at R = 12R⋆, where the flow is most stable. The latter is computed across the disk height, and corresponds to the total mass accretion rate available for distribution in the system. The component ṀSW at the same stellar rotation rate is shown together with corresponding torques in Fig. 9. Note: the y-label multiplication factor is given in the left upper corner of the panels.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


