Fig. 2.
Download original image
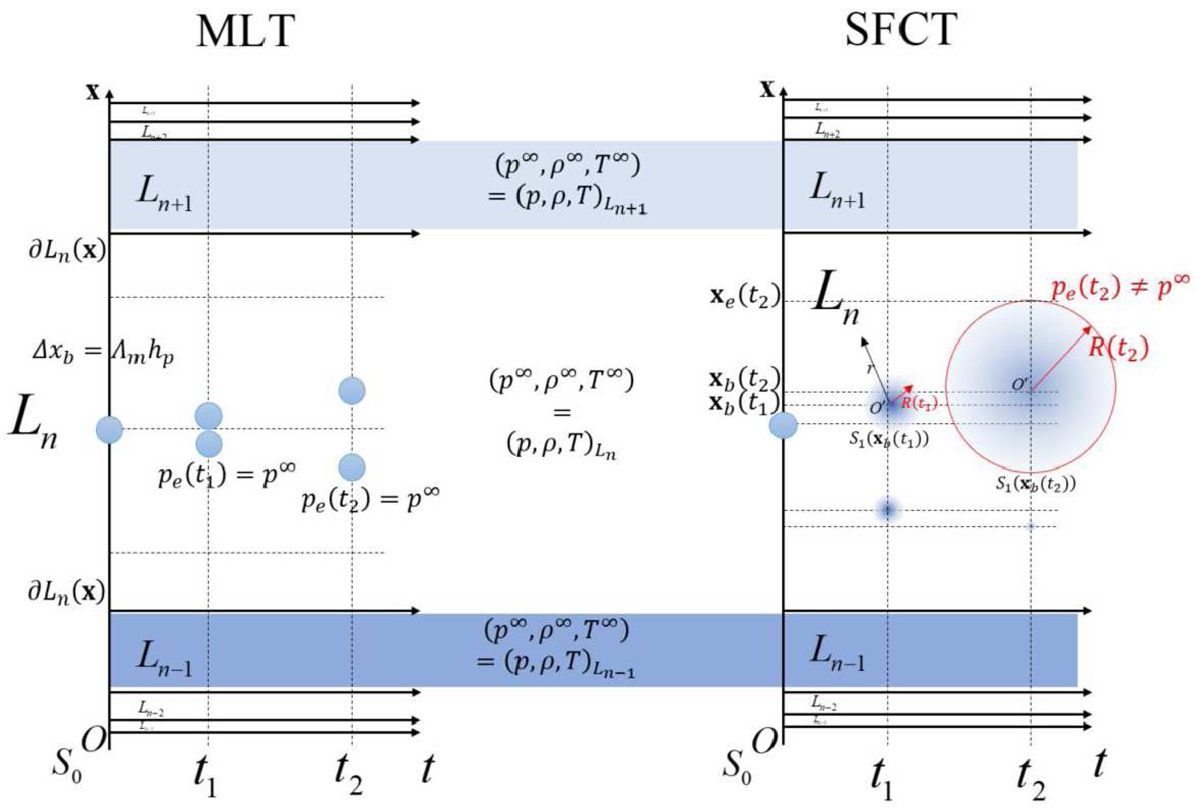
Artistic representation of temporal evolution of a convective element. The star is a superposition of m layers in hydrostatic equilibrium. The generic layer, Ln, is defined by the hydrostatic pressure, density, and temperature (p,ρ,T)Ln. These values are assumed to be time-independent and far away from the convective element, i.e., for every layer ![]() . Vice versa, each convective element is never in hydrostatic equilibrium with its medium, and the pressure, temperature, and density at the surface of a convective element are {pe(t),ρe(t),Te(t)}≠{p∞,ρ∞,T∞}. Upper and lower borders of a layer are indicated by ∂Ln = ∂Ln(x). Data are from Pasetto et al. (2019).
. Vice versa, each convective element is never in hydrostatic equilibrium with its medium, and the pressure, temperature, and density at the surface of a convective element are {pe(t),ρe(t),Te(t)}≠{p∞,ρ∞,T∞}. Upper and lower borders of a layer are indicated by ∂Ln = ∂Ln(x). Data are from Pasetto et al. (2019).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


