Fig. 15.
Download original image
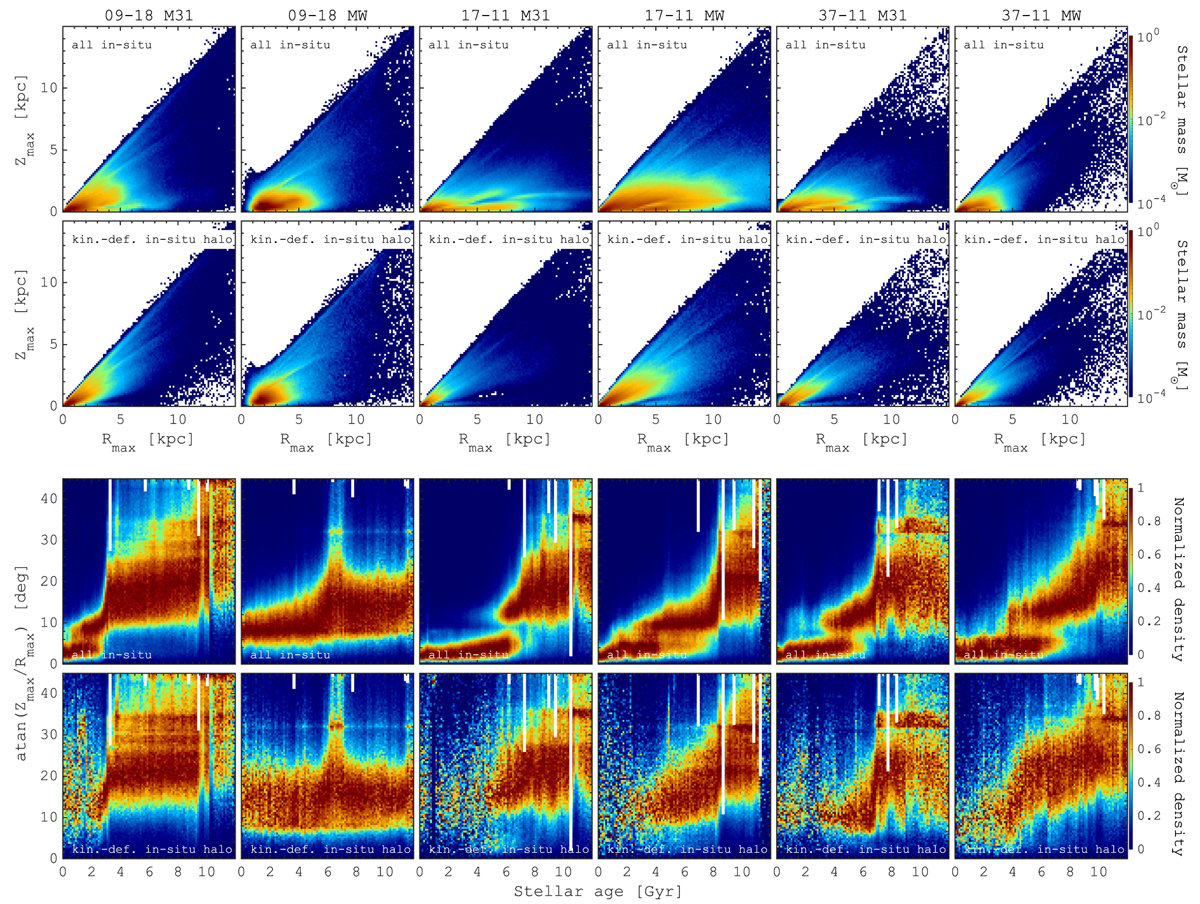
Orbital structure of in situ stellar halo. Top: stellar density distribution in Rmax − Zmax coordinates for all in situ stars (first row) and kinematically defined (see Toomre diagram in Fig. 9) in situ stellar halo (second row). Bottom: distribution of the angles between Rmax − Zmax as a function of the stellar age for all in situ stars (third row) and kinematically defined stellar halo (fourth row). The white vertical lines highlight five of the most significant mergers (M1–M5), in terms of the stellar mass ratio. Similar to a number of recent MW studies (see, e.g, Haywood et al. 2018; Koppelman et al. 2021) the HESTIA galaxies reveal a number of wedges in Rmax − Zmax coordinates. The bottom rows show how these wedges emerge over time. We find that the individual structures in Rmax − Zmax are made of stars predominantly made of stars that formed in between the significant merger events, suggesting a similar origin for similar structures in the MW.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


