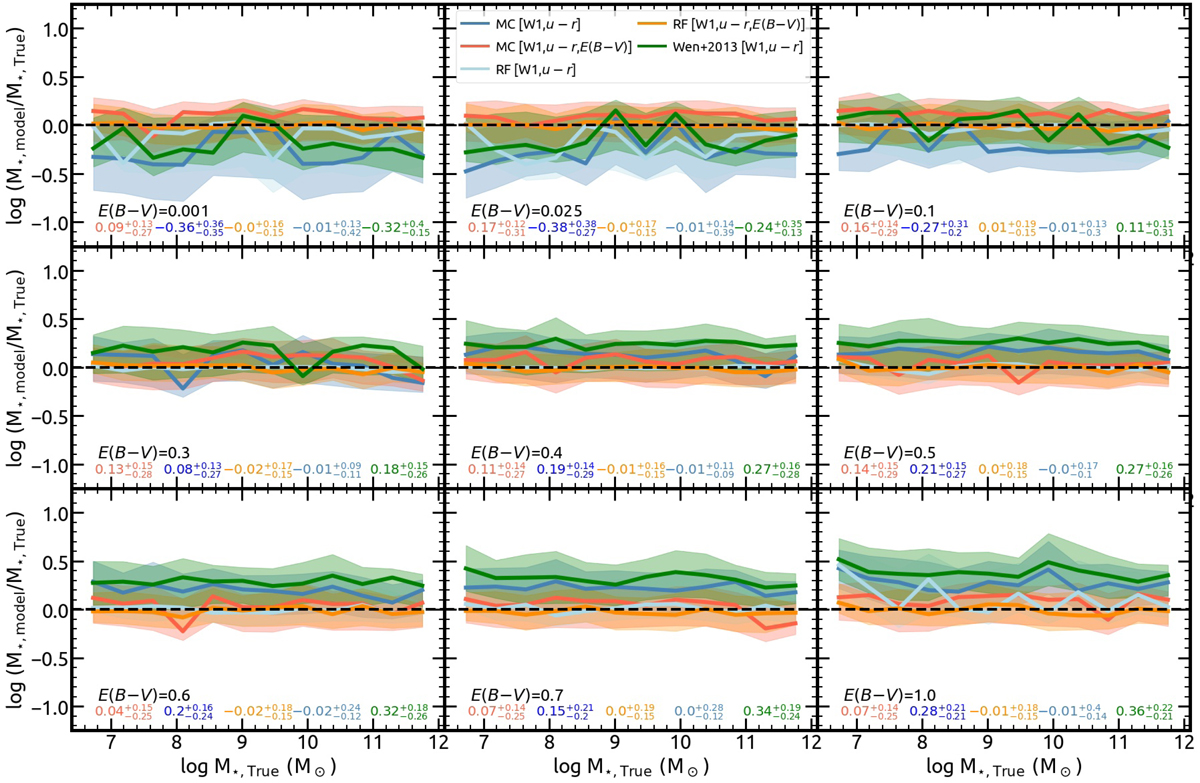
Fig. 8.
Download original image
Comparison between the true M⋆ as given by the CIGALE output, and the best-fit models of Eq. (6) (MC; Table 3), and the random forest machine learning method (RF) using the WISE band-1 and the u − r color. The y-axis represents the logarithm of the ratio between the M⋆ of each model and the true M⋆, thus the black dashed line at zero represents equality. Blue and red colors show the extinction-independent, and extinction-dependent relation of Eq. (6) respectively. With light-blue and orange colors are the extinction-independent, and extinction-dependent models based on the RF method respectively. The M⋆ calculated based on the mass-to-light conversion from Wen et al. (2013) is also shown with green color. The lines represent the distribution modes and the shaded areas the 68% percentiles as a function of the log M⋆ true. Each panel shows the comparison of galaxy models with one of the discrete E(B − V) values, shown in the bottom left corner of each panel. This comparison is performed with the uniform-E(B − V) sample, therefore, there is an equal number of sources for each extinction value. At the bottom of each panel are the modes and 68% percentiles of the log M⋆model/M⋆, True distribution for all galaxy models with the specific E(B − V), shown with corresponding colors to the relations used to derive the M⋆. These comparisons are also summarized in Table 4.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


