Fig. 2.
Download original image
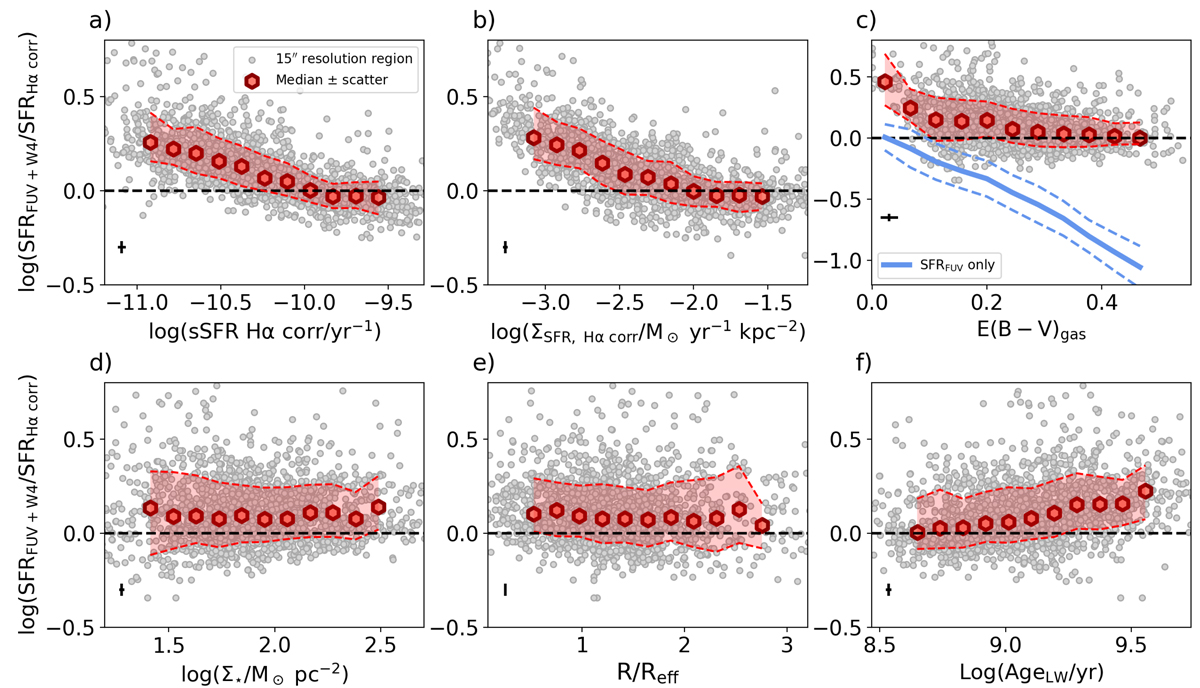
Dependence of the ratio of the SFR measured from FUV+W4 (and the Leroy et al. 2019 coefficient) and that measured from attenuation-corrected Hα on various physical properties for a sample of 1759 ∼ kpc sized regions taken from the 19 galaxies of the PHANGS-MUSE sample: (a) sSFR, (b) SFR surface density (both measured from attenuation-corrected Hα), (c) E(B − V) of the ionised gas measured from the Balmer decrement, (d) stellar mass surface density, (e) deprojected galactocentric radius normalised to Reff, (f) light-weighted mean age of the stellar population, derived from fits to the MUSE stellar continuum. The grey points represent individual ∼15″ regions, and the red hexagons and dashed red lines represent the median and scatter (16th − 84th percentiles) of the distribution. In panel c, we also show the result of calculating the SFR from the FUV flux, without considering the IR term (blue lines). This demonstrates that the inclusion of the IR term correctly reproduces the Hα-based SFR for highly attenuated regions, but it overestimates the attenuation level for regions with a low Balmer decrement. These trends are consistent with an increasing contamination from old stellar population to the dust heating at lower SFR levels.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


