Open Access
Table 1
List of symbols and notation.
| Symbol | Quantity |
|---|---|
| t | Time |
| dt | Time-step, small time interval |
| x, y, z | Cartesian coordinates |
| V | Volume |
| h = ∆a | Thickness of spherical shell |
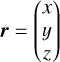 |
Position vector |
| r | Radial distance |
| υ = ṙ | Velocity vector |
| υ | Speed |
| d=r2−r1 | Difference position |
| d | Distance |
| u = υ2 − υ1 | Difference velocity |
| u | Relative speed |
| w = υ1 × υ2 | |
| G | Newton’s constant |
| M | Mass of central body |
| S | Radius of central body |
| m | Particle mass |
| s | Particle radius |
| t0 | Particle creation time |
| T | Orbit time |
| ω = 2π/T | Mean motion |
| Tcoll | Time between collisions |
| Tscat | Time between close encounters |
| Tprec | Precession period/time scale |
| Tsim | Total simulated time |
| a, b | Semimajor-, semiminor-axis |
| c = aϵ | Semi-focal separation |
| ℓ | Semi-latus rectum |
| r0 | Particle creation point |
| S | Spin angular momentum |
| L | Orbital angular momentum |
| K = L1 × L2 | Direction of nodal line |
| ϵ | Eccentricity vector |
| ϖ | Argument of periapsis |
| Ω | Ascending node |
| I | Inclination |
| v | True anomaly |
| E | Eccentric anomaly |
| ℛ | Rotation matrix |
| N | Number of particles |
| κ | Number of fragments |
| i, j | Particle indices |
| k, l | Rounds to collision |
| n | Counter |
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


