Fig. 6
Download original image
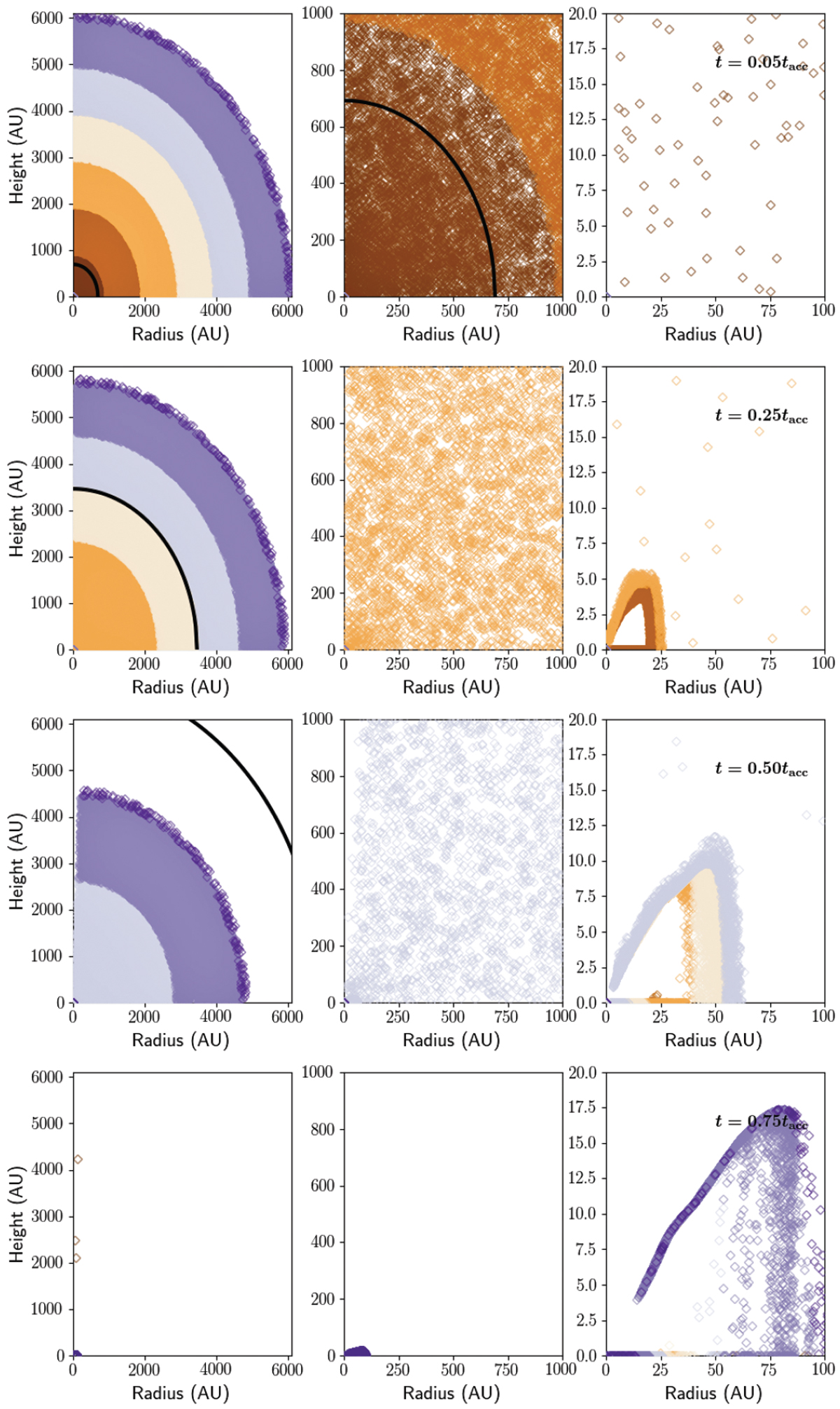
Collapse of dust parcels in the Ref-med model. The colour and time steps are the same as in Figs. 4 and 5, but the x-axis scale changes in the right panels. While the overall collapse is over a similar timescale as in the Std-med model, the disk build-up and subsequent evolution in the disk is different. The gas disk is larger in the reference model, and dust grains fall predominately at the outward edge of the disk on average. Viscous spreading is still present in the embedded disk, but most of the dust evolution is inward via radial drift. At late times, the dust ring is therefore extended, and most of the dust is inward of the ring in the midplane or at the upper surface of the disk. For comparison, the black line shows an estimate of the location of the gas rarefaction wave defined by x = 1.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


