Fig. B.3
Download original image
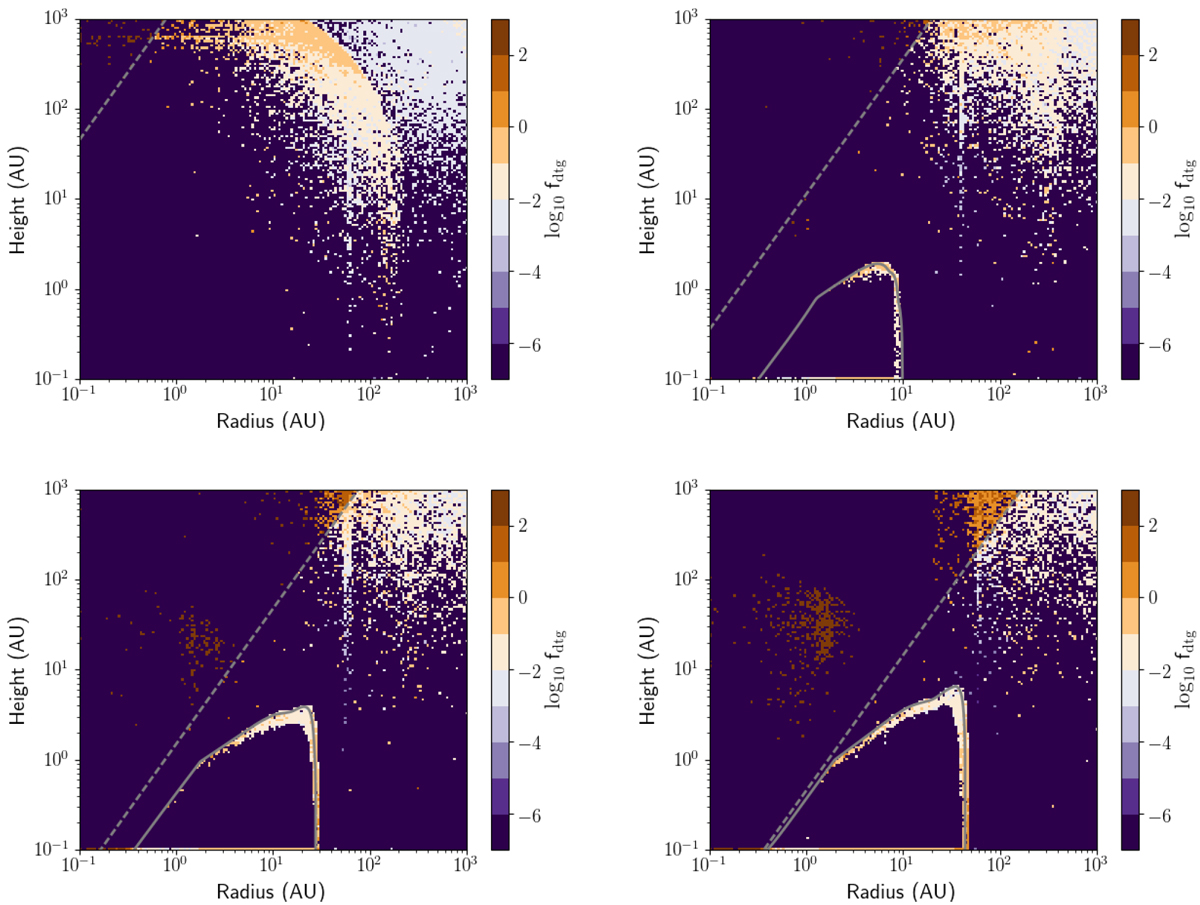
Same as Figure 8, but for the Std-sml model. Because of the small dust grains used in this model, the collapse and evolution in the disk are more strongly coupled to the gas. They therefore tend to evolve in a similar was as the gas, creating mainly ISM dust-to-gas ratios in the midplane of the disk. In the thin regions around the surface of the disk, the sudden pressure change captures the dust, similarly to typical dust traps in class II disks.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


