Fig. 4
Download original image
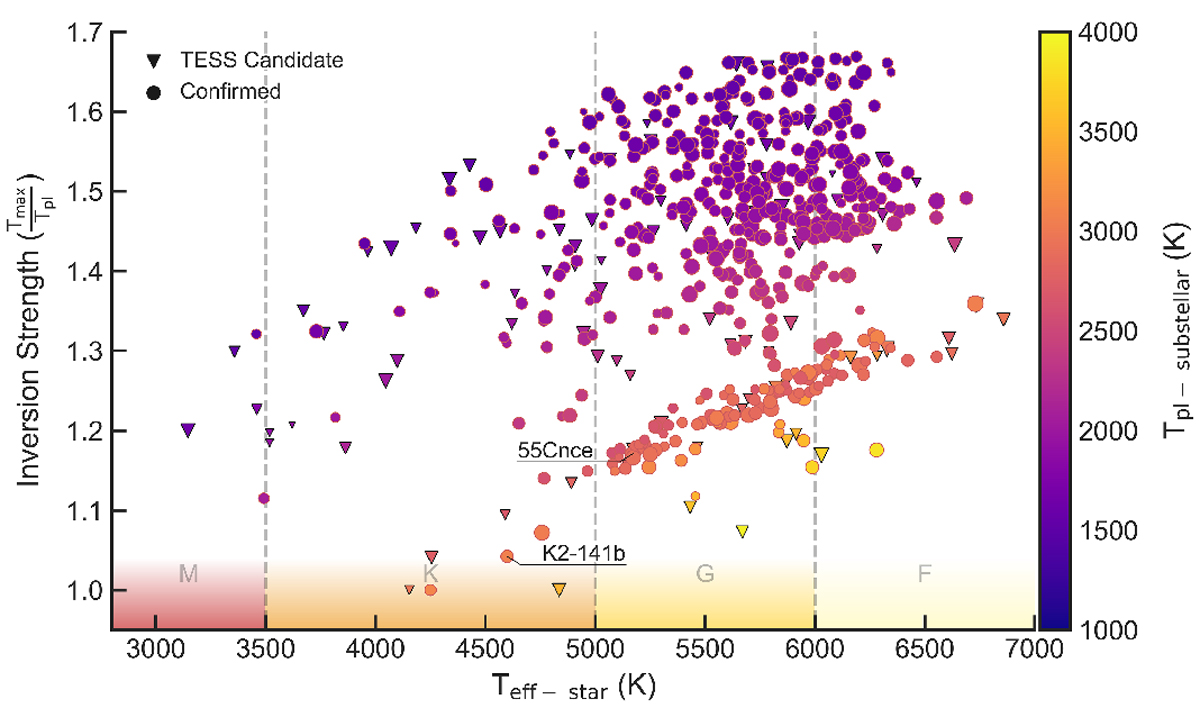
Thermal inversion strength relation with the temperature of the stellar host and the -stellar temperature of the planet. Inversion strength is the ratio of the maximum atmospheric temperature with the surface temperature of the planet. In most cases the maximum temperature coincides with the uppermost regions. Inversions become greater with increasing stellar temperature and is anti-correlated with the temperature of the planet. Silicate atmospheres become fully opaque at around 2600 K surface temperature, causing a change in atmospheric structure (isothermal lower layer), indicated via clustered planets separated via a distinct gap.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


