Fig. 13
Download original image
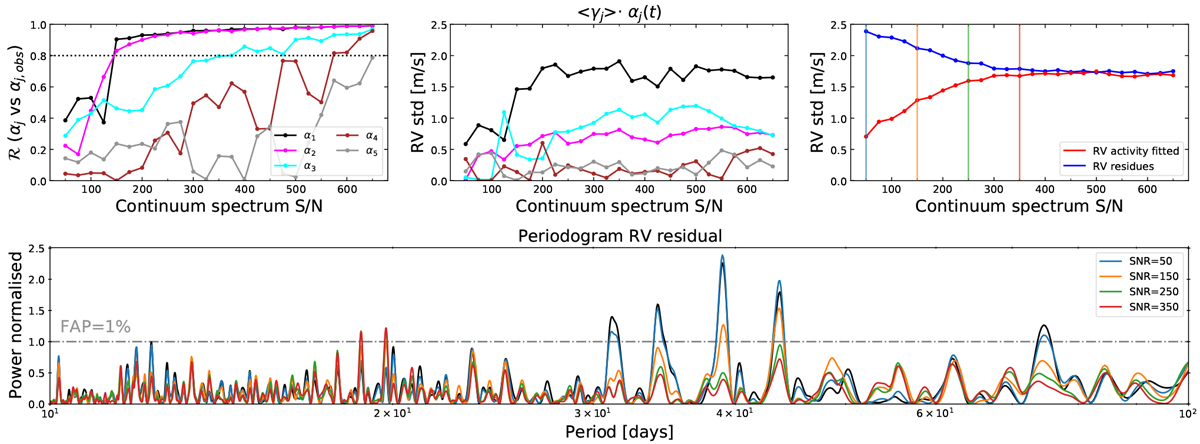
Noise injection tests performed on HD 128621 to evaluate the performance of our shell framework in mitigating stellar activity depending on the continuum signal-to-noise ratio, S∕Ncont. The cross-validation algorithm to select only shell basis components with significant variance was disabled and five componentswere used for the fitted model. Top left: correlation between the noise-affected shell basis coefficients αj and their respective coefficients without extra-noise injected αj,obs. A shell basis component can be considered as recovered once its related coefficient αj exceeds a correlation value with αj,obs higher than ![]() (dotted line). This threshold was selected as the level that the shell basis component α5, which is associated with noise in the observations, never reaches. Top middle: RV rms of the projected αj (t) on the raw RV time series. Top right: RV rms of the residual RVs linearly decorrelated from the shell basis coefficients αj (blue), as well as RV rms of the fitted RV activity model (red). The result for four different interesting S∕Ncont values (vertical lines): 50, 150, 250 and 350 are discussed in detail in the text. Bottom: periodograms of the residual RVs obtained after our shell framework correction for the four selected S∕Ncont levels. The periodogram of the uncorrected RVs are displayed in black as a comparison. The power of each periodogram was normalised by the 1% FAP level.
(dotted line). This threshold was selected as the level that the shell basis component α5, which is associated with noise in the observations, never reaches. Top middle: RV rms of the projected αj (t) on the raw RV time series. Top right: RV rms of the residual RVs linearly decorrelated from the shell basis coefficients αj (blue), as well as RV rms of the fitted RV activity model (red). The result for four different interesting S∕Ncont values (vertical lines): 50, 150, 250 and 350 are discussed in detail in the text. Bottom: periodograms of the residual RVs obtained after our shell framework correction for the four selected S∕Ncont levels. The periodogram of the uncorrected RVs are displayed in black as a comparison. The power of each periodogram was normalised by the 1% FAP level.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


