Fig. 1.
Download original image
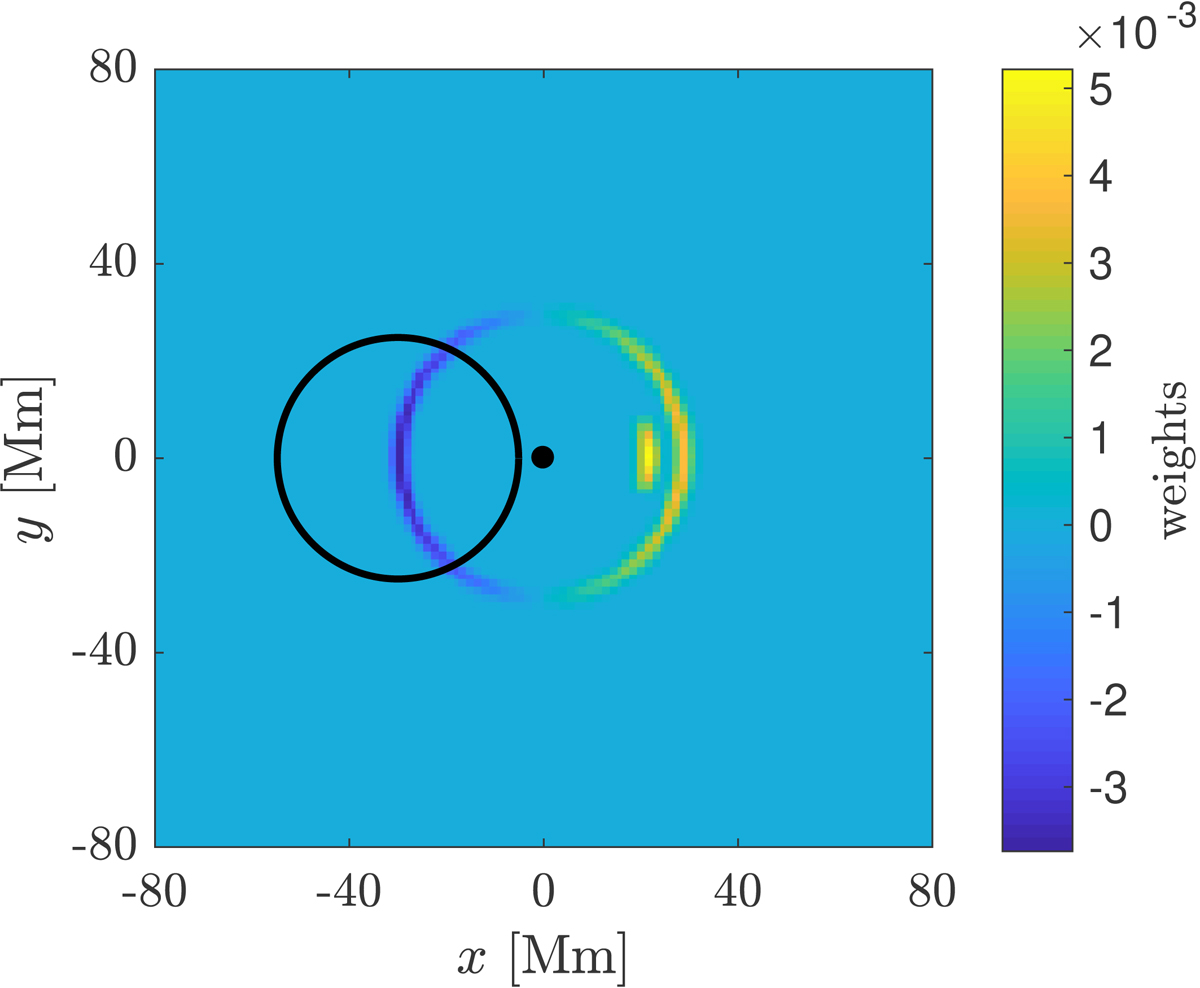
Examples of the annulus (the outer annulus) and the arc (the inner arc) averaging geometries. The black dot is the point where the travel time is measured. The colours correspond to the weights of the averaging geometries. The black circle delimits the artificial active region. The annulus geometry averages the quiet and the active regions because of its two-sided character; the observed point in the one-sided arc geometry is not affected by the active region. For display purposes, the radii of the averaging geometries differ, the full width at half maxima (FWHMs) of the Gaussian annuli were enlarged, and the weights of the arc geometry were divided by 12.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


