Fig. 15.
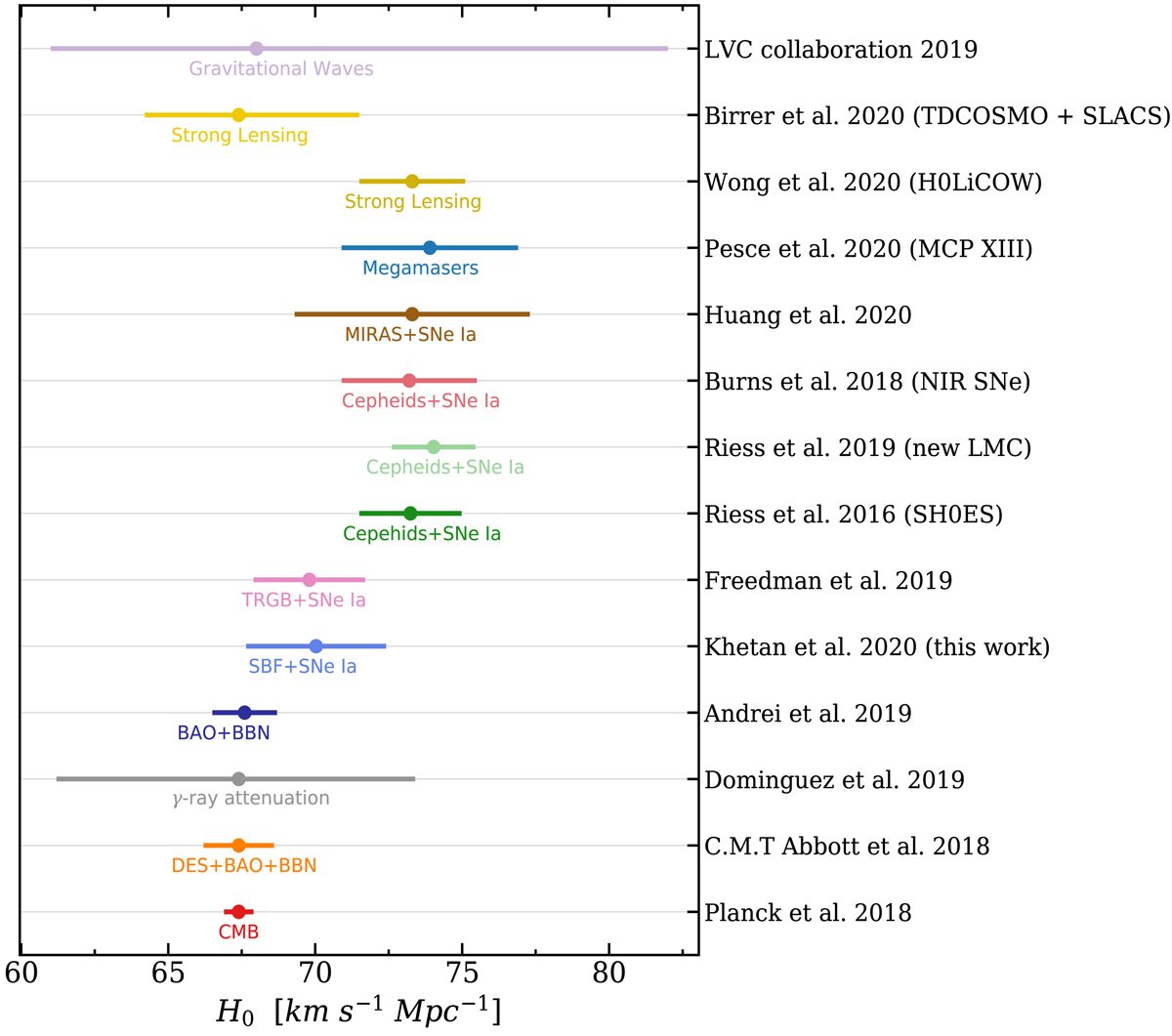
Compilation of Hubble constant values obtained using different observations and techniques from the recent literature including the value from this work. The literature references are written on the y-axis. Two independent estimates from early Universe (Planck Collaboration XIII 2016; Abbott et al. 2018) are shown at the bottom. The next is an estimate using extragalactic background light γ ray attenuation (Domínguez et al. 2019) and another from BAO at all redshifts + BBN estimate (Cuceu et al. 2019). Then we show measurements from SNe Ia calibrated with TRGB (Freedman et al. 2019), SNe Ia calibrated with Cepheids (SH0ES sample, Riess et al. 2016, 2019), using near-infrared (NIR) filters (Burns et al. 2018) and SNe Ia with Mira variables (Huang et al. 2020). Then we show the H0 values estimated using 6 masers in the Hubble flow (Pesce et al. 2020). The next H0 value shown is inferred via gravitational lensing time delays using six lensed quasars (Wong et al. 2020) and a more recent value obtained using 40 strong lenses (Birrer et al. 2020). Finally we shows the H0 derived with gravitational-wave signals from binary compact object mergers (Abbott et al. 2019).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


