Fig. 5.
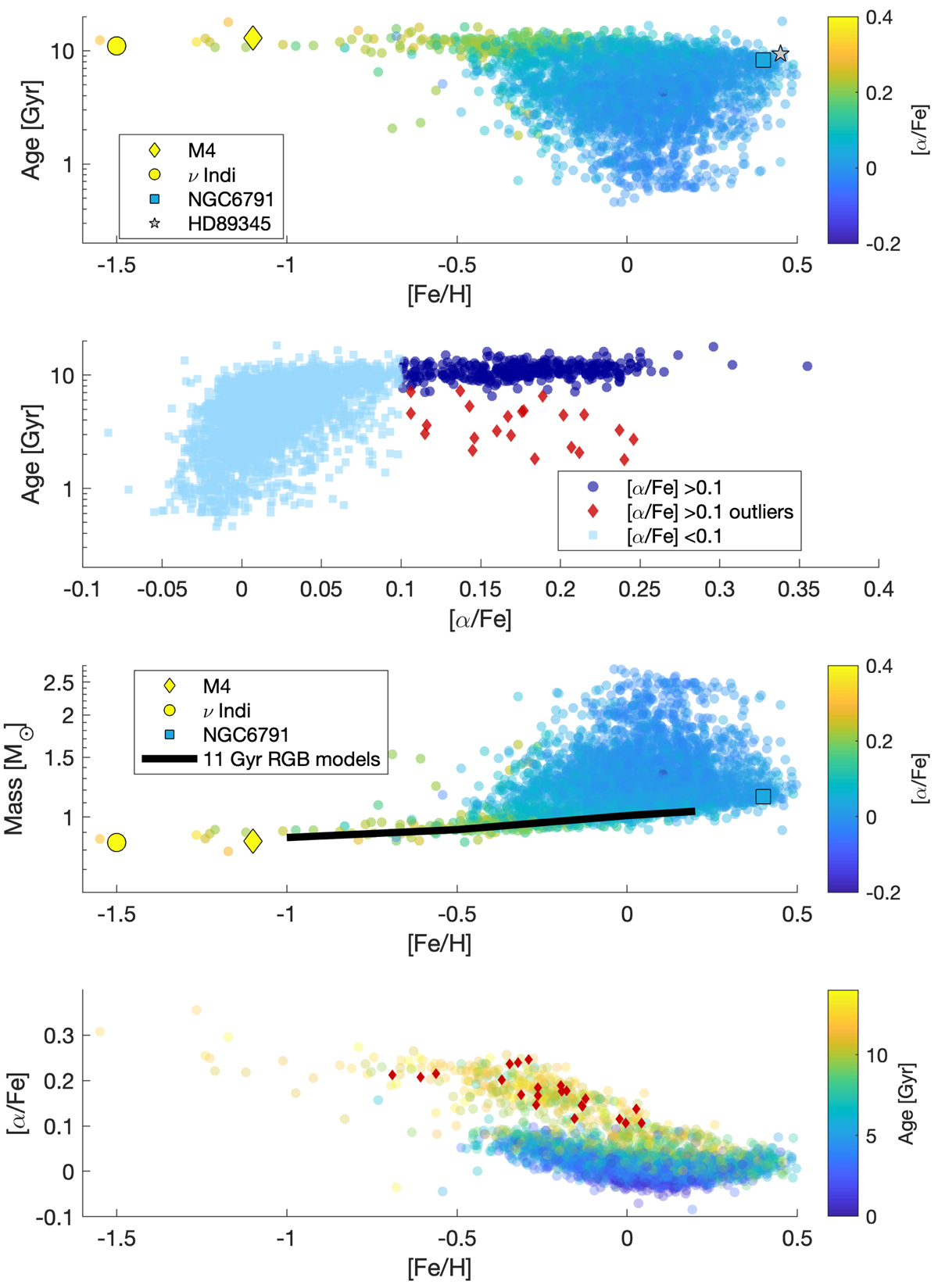
Age-mass-chemical-composition scatter plots of stars in our sample (R < 11 R⊙ and including RC stars with M > 1.2 M⊙, see main text for details). Black crosses indicate typical uncertainties on the relevant measured/inferred properties. Top panel: age vs. [Fe/H]. The colour represents [α/Fe]. Upper middle panel: age vs. [α/Fe]. Red dots denote α-rich stars that are considered outliers based on their mass or age (see Sect. 5.2 for the criterion used). Lower middle panel: stellar mass versus [Fe/H]. The mass of 11-Gyr-old RGB models of different metallicity is shown as a solid line. Bottom panel: [α/Fe] versus [Fe/H], where the age is represented by colour. Red dots identify age/mass outliers among the α-rich population. Top and lower middle panels: mass, chemical composition and inferred age for eclipsing binaries in the old-open cluster NGC 6791 (Brogaard et al. 2012), the old metal-rich subgiant HD 89345 (Van Eylen et al. 2018, [α/Fe] is not available for this object), and in well-studied metal-poor objects: RGB stars in the globular cluster M 4 (Kaluzny et al. 2013; Miglio et al. 2016) and the nearby subgiant ν Indi (Chaplin et al. 2020).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


