Fig. 2
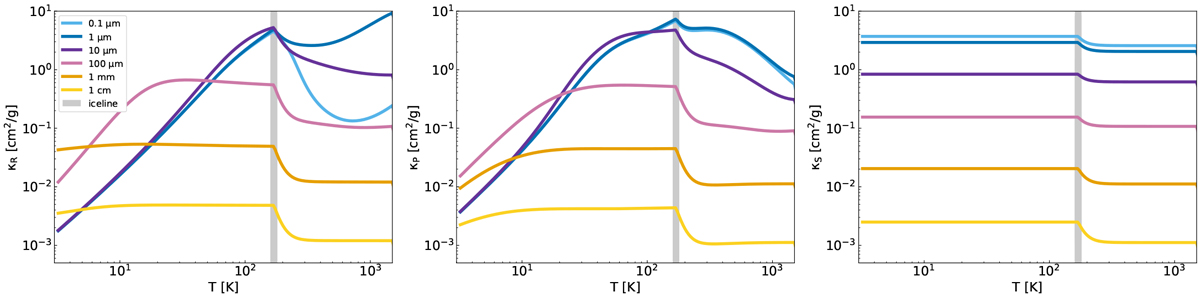
Rosseland, Planck, and stellar mean opacities (from left to right) as a function of temperature for grains of sizes 0.1, 1, 10, 100 μm, 1 mm, and 1 cm. They are independent of the gas density because they are dominated by the dust component. These values were calculated using RADMC-3D for a mixture of 50% silicates, 50% ice, and disc dust-to-gas ratio of 1%. The gray vertical line shows the location of the water iceline transition (170 K ± 10 K), causing a transition in opacity due to the evaporation/condensation of dust grains.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


