Fig. 9
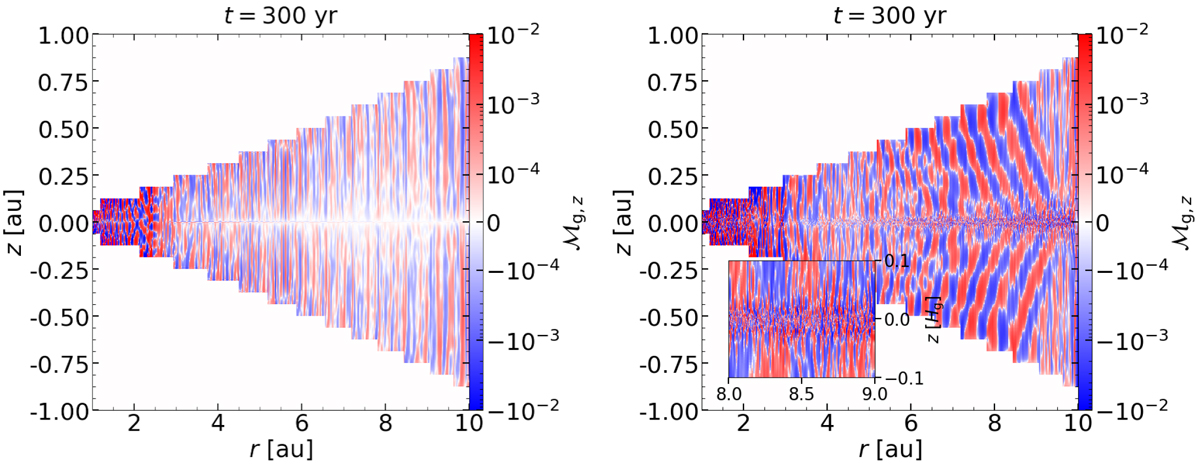
Mach number of the vertical gas velocity as a function of r and z in simulations of dust and a locally adiabatic gas. The Mach number at radii of less than ~ 3 au is similarlyhigh in the simulation without (adi_Lr=9au; left panel) or with dust (adi_Z=0.02_Lr=9au; right panel). This is in spite of the streaming instability operating in the latter simulation, but not in the former one. At larger radii in the simulation that includes dust, the streaming instability induces large-scale perturbations with ![]() away from the midplane. These perturbations are similar in shape to the ones caused by the vertical shear instability, but they are weaker, are bent inwards rather than outwards, and are not symmetric with respect to the midplane (compare with Fig. 1). In the inlay, which extends to 0.1 gas scale heights Hg above and below the midplane, small-scale perturbations with
away from the midplane. These perturbations are similar in shape to the ones caused by the vertical shear instability, but they are weaker, are bent inwards rather than outwards, and are not symmetric with respect to the midplane (compare with Fig. 1). In the inlay, which extends to 0.1 gas scale heights Hg above and below the midplane, small-scale perturbations with ![]() in the midplane can be seen.
in the midplane can be seen.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


