Fig. 10
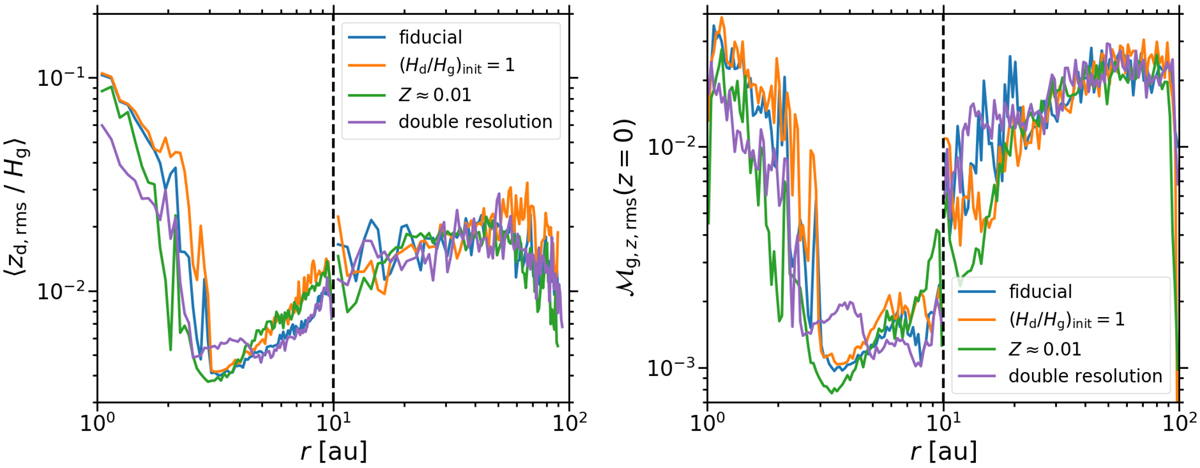
Ratio of the dust scale height, as the root mean square of zd, to the gas scale height Hg (left panel) as well as mass-weighted root mean square of ![]() in the midplane (right panel). Both quantities are depicted as functions of r. To compute the root mean square, we average over 50 or 500 yr after the dust scale height has reached an equilibrium value in the simulation domains spanning 1 au ≤ r ≤ 10 au or 10 au ≤ r ≤ 100 au, respectively. The dashed line marks the boundary between these domains. The model with an initial dust-to-gas scale height ratio of
in the midplane (right panel). Both quantities are depicted as functions of r. To compute the root mean square, we average over 50 or 500 yr after the dust scale height has reached an equilibrium value in the simulation domains spanning 1 au ≤ r ≤ 10 au or 10 au ≤ r ≤ 100 au, respectively. The dashed line marks the boundary between these domains. The model with an initial dust-to-gas scale height ratio of ![]() , a dust-to-gas surface density ratio of Z = 2%, and the fiducial resolution (blue line) is shown together with the models that deviate from this fiducial one in that
, a dust-to-gas surface density ratio of Z = 2%, and the fiducial resolution (blue line) is shown together with the models that deviate from this fiducial one in that ![]() , that Z = 1% (green line),or that the initial and maximum resolution are doubled (purple line). While both the dust scale height and the Mach number depend on the radius, they are largely independent of the initial dust scale height, the surface density ratio, and the resolution.
, that Z = 1% (green line),or that the initial and maximum resolution are doubled (purple line). While both the dust scale height and the Mach number depend on the radius, they are largely independent of the initial dust scale height, the surface density ratio, and the resolution.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


