Fig. 3
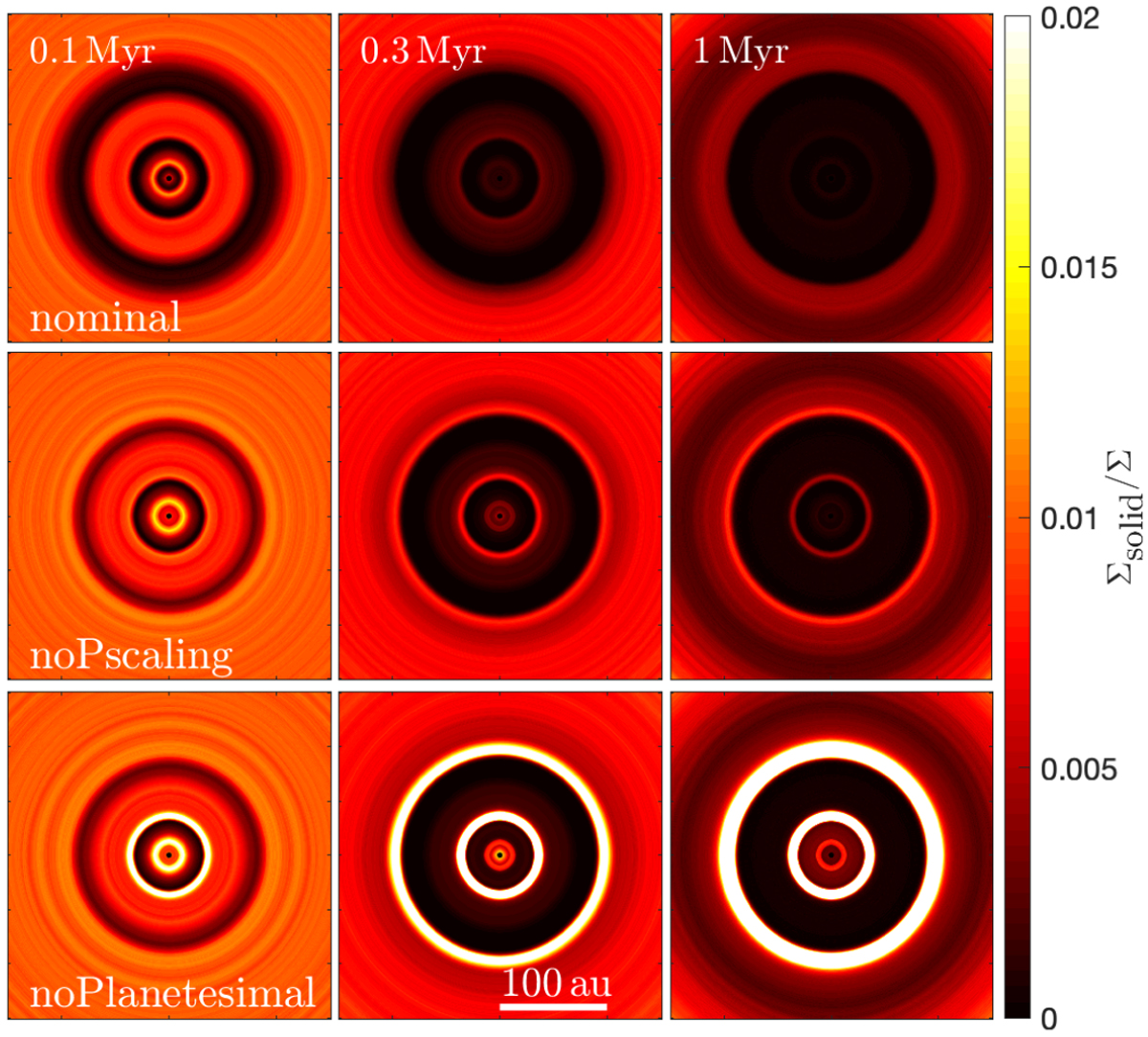
2D symmetric disc images of the evolution of the solid-to-gas surface density (excluding the formed planetesimals) for three different versions of the nominal model: the nominal model (top row), the nominal model with planetesimal formation but with no dependency on the pressure gradient (middle row), and the nominal model without planetesimal formation (bottom row). In the nominal model, essentially everything that enters the pressure bump is converted into planetesimals, resulting in a large cavity in the distribution of dust and pebbles. When the pressure dependence is neglected, the critical density required to trigger the streaming instability increases, and we see some rings in the dust and pebble distribution. When planetesimal formation is removed completely, we are left with three rings in which the dust and pebble density is very high.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


