Fig. A.1.
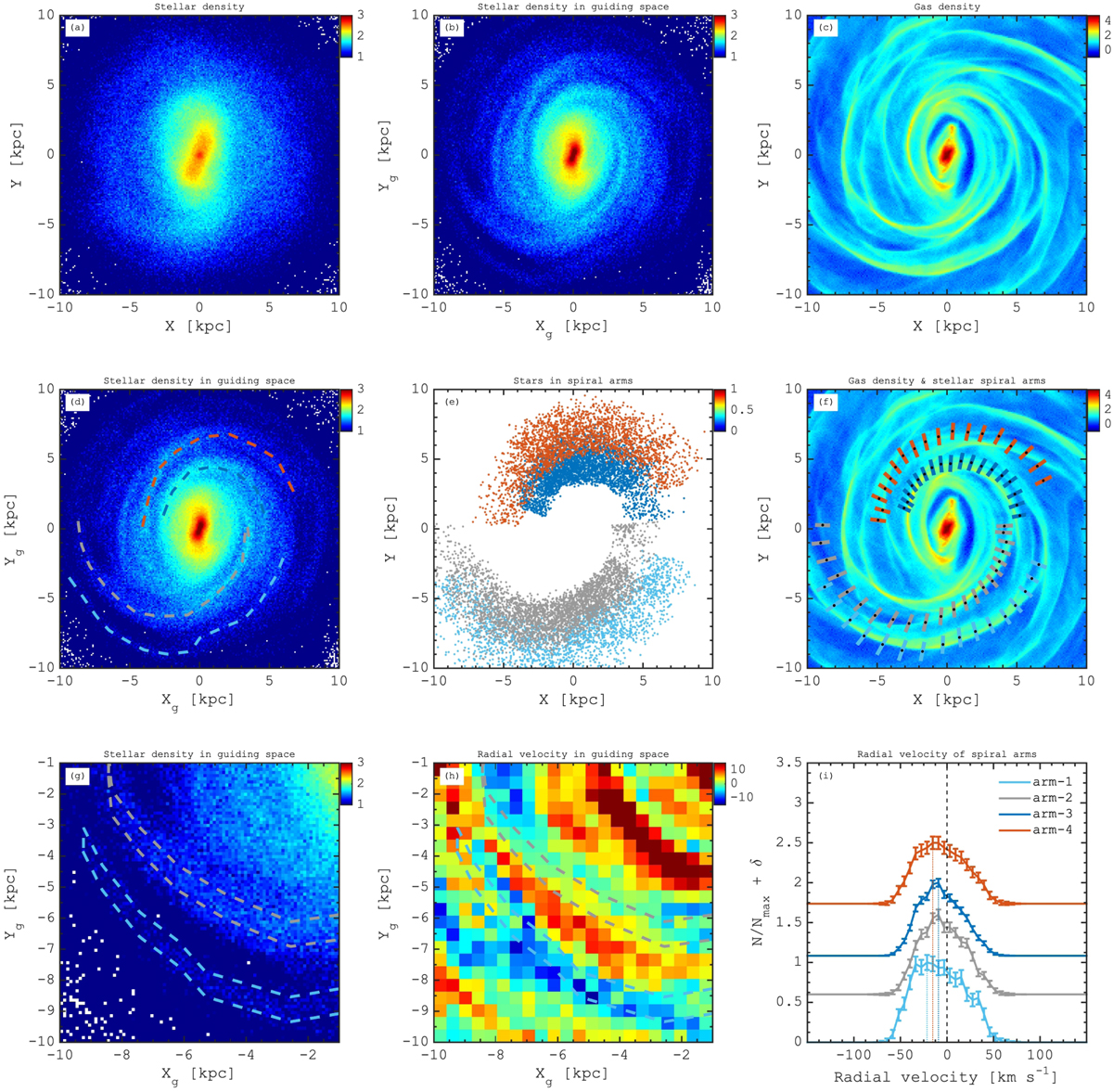
Milky Way-type galaxy simulation (Model I) showing the behaviour of spiral arms. Panels a and b: face-on stellar surface density in spatial coordinates and in the guiding phase-space, respectively. Panel c: face-on surface density of gas. Panel d: same as (b), but with the coloured lines depicting the position of four spiral arms features. Panel e: spatial distribution of star particles associated with the spiral-arm features detected guiding space. Colours of points correspond to the colour of lines in (d). Panel f: gas surface density distribution with a position of stellar spiral arms overplotted. Panel g: zoom-in of the guiding space containing two prominent spiral arms highlighted by the coloured lines. Panel h: distribution of the mean radial velocity in the zoomed-in region of the guiding space where the contours show the spiral arm location. Panel i: distribution of the radial velocities of stars in four spiral arms identified in frames (d) and (e) where the spiral arms stars have skewed distribution with negative mean values. The errors in the radial velocity measurements are determined from the scatter around the mean value, using the standard deviation of the measurements. The kinematical features presented here confirm that the structures with similar kinematics found in the guiding space of the Milky Way are the spiral arms.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


