Fig. 1.
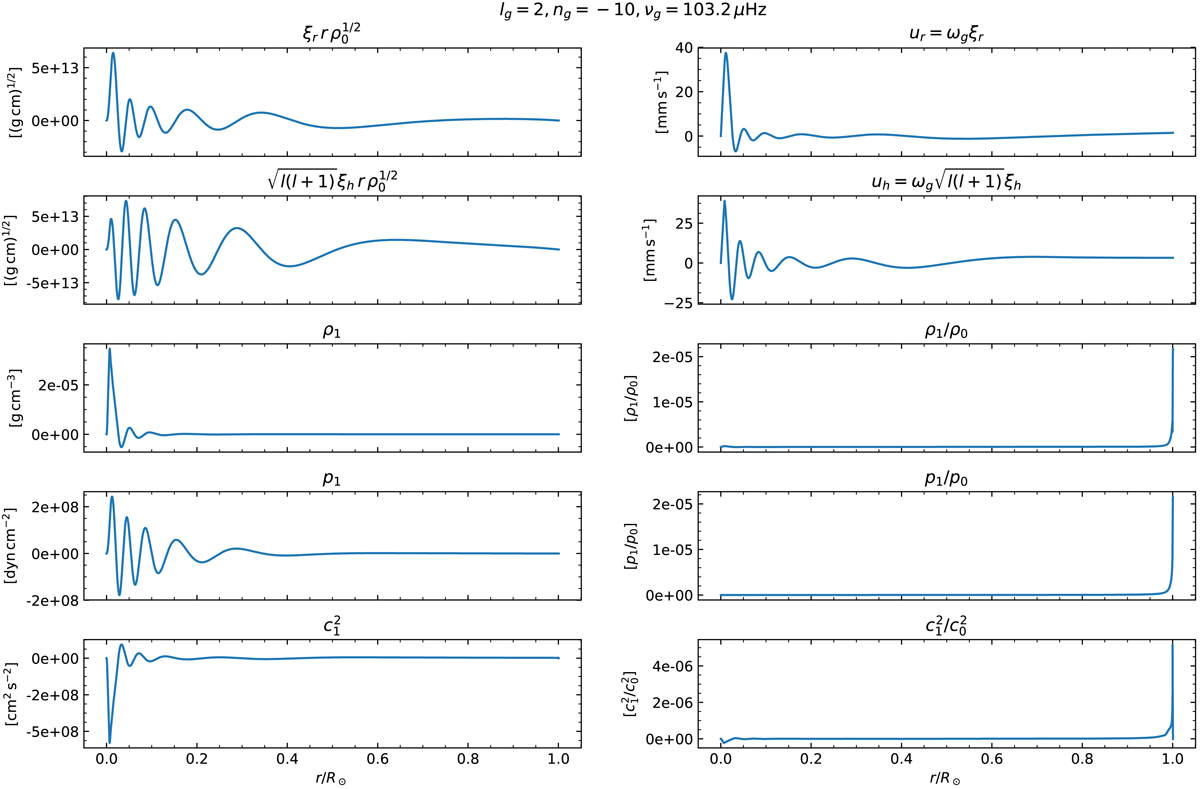
Eigenfunctions and Eulerian perturbations to solar structure for a typical g mode with lg = 2, ng = −10, νg = 103.2 μHz (compare to Fig. 5.10 in Christensen-Dalsgaard 2003). The mode was normalised to a surface amplitude of 1 mm s−1, which is at the order of observational upper limits (e.g. Appourchaux et al. 2010). Displayed are (from top to bottom) radial and horizontal eigenfunctions, and the Eulerian perturbations to density, pressure, and squared sound speed. Left column: kinetic energy density and absolute changes to solar structure caused by the mode are centred near the solar core. Right column: relative changes to solar structure are very small, and in the case of density, pressure, and sound speed, reach the largest values near the surface. The exact behaviour of the relative Eulerian changes to solar structure at the surface depends on the choice of boundary condition used in the eigenfunction computation.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


