Fig. 7.
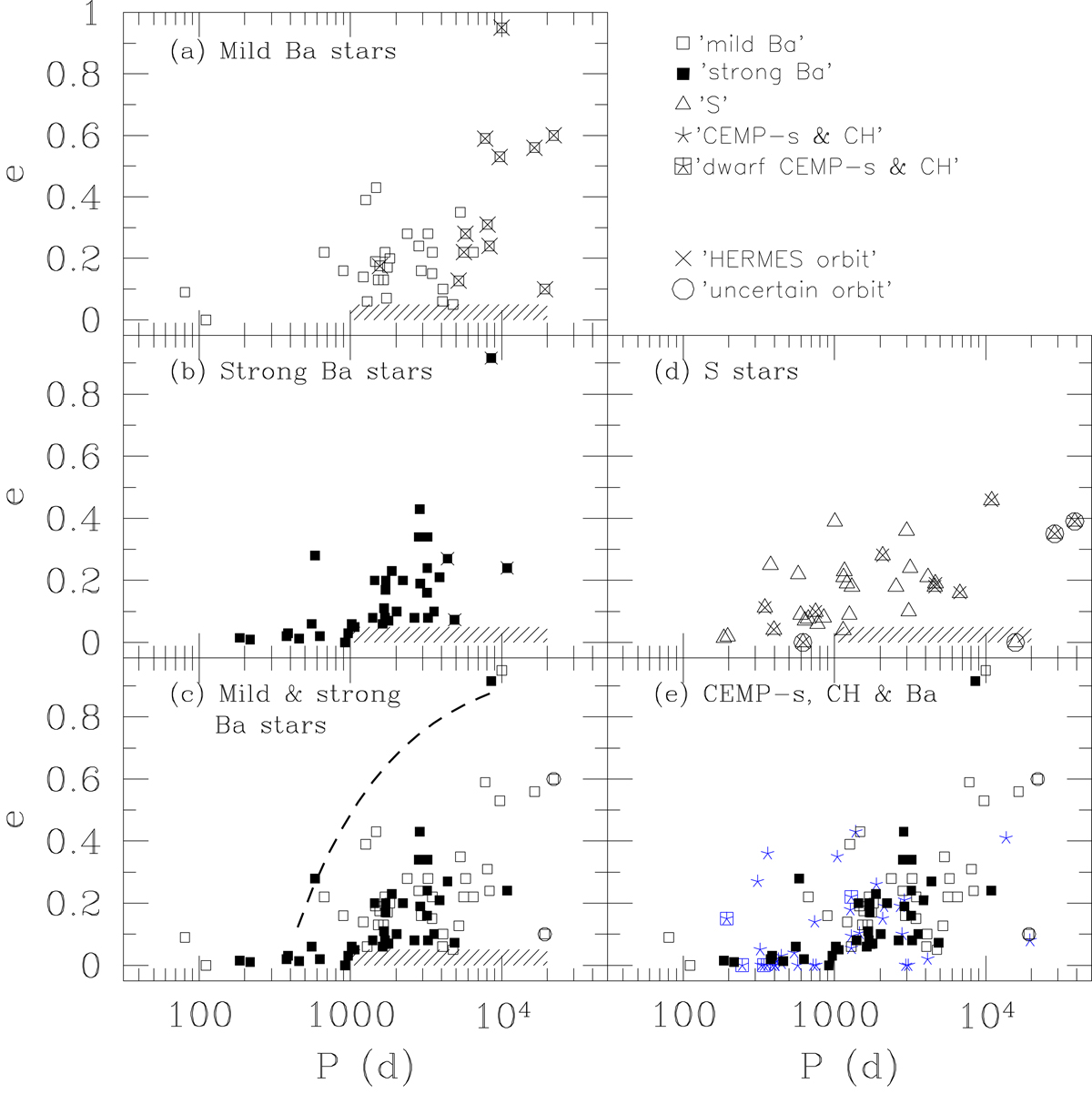
Eccentricity–period diagrams for various samples. The meaning of the various symbols is given in the upper right panel. (a) Mild barium stars; (b) strong barium stars; (c) mild (open squares) and strong (filled squares) barium stars plotted together. The dashed line corresponds to the upper envelope of the data points, well represented by the condition 143 R⊙ = RRoche = A (1 − e) [0.38 + 0.2log(MBa/MWD)], corresponding to RLOF occurring at periastron for a star of radius 143 R⊙. A is the semi-major axis of the orbit, linked to the orbital period P through the third Kepler law, adopting component masses of MBa = 2 M⊙ and MWD = 0.65 M⊙; (d) S stars (triangles). The S star HD 184185, with P ∼ 15723 d and e ∼ 0, falls in the low e – long P gap (represented by the hatched area), probably as a consequence of its still-uncertain orbital parameters; (e) as in (c), adding CEMP-s and CH stars (blue 5-branch crosses; squared crosses correspond to carbon dwarfs from Jorissen et al. 2016a). The dwarf CEMP star HE 0024−2523 with an orbital period of 3.4 d falls outside the graph boundaries.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


