Fig. 8.
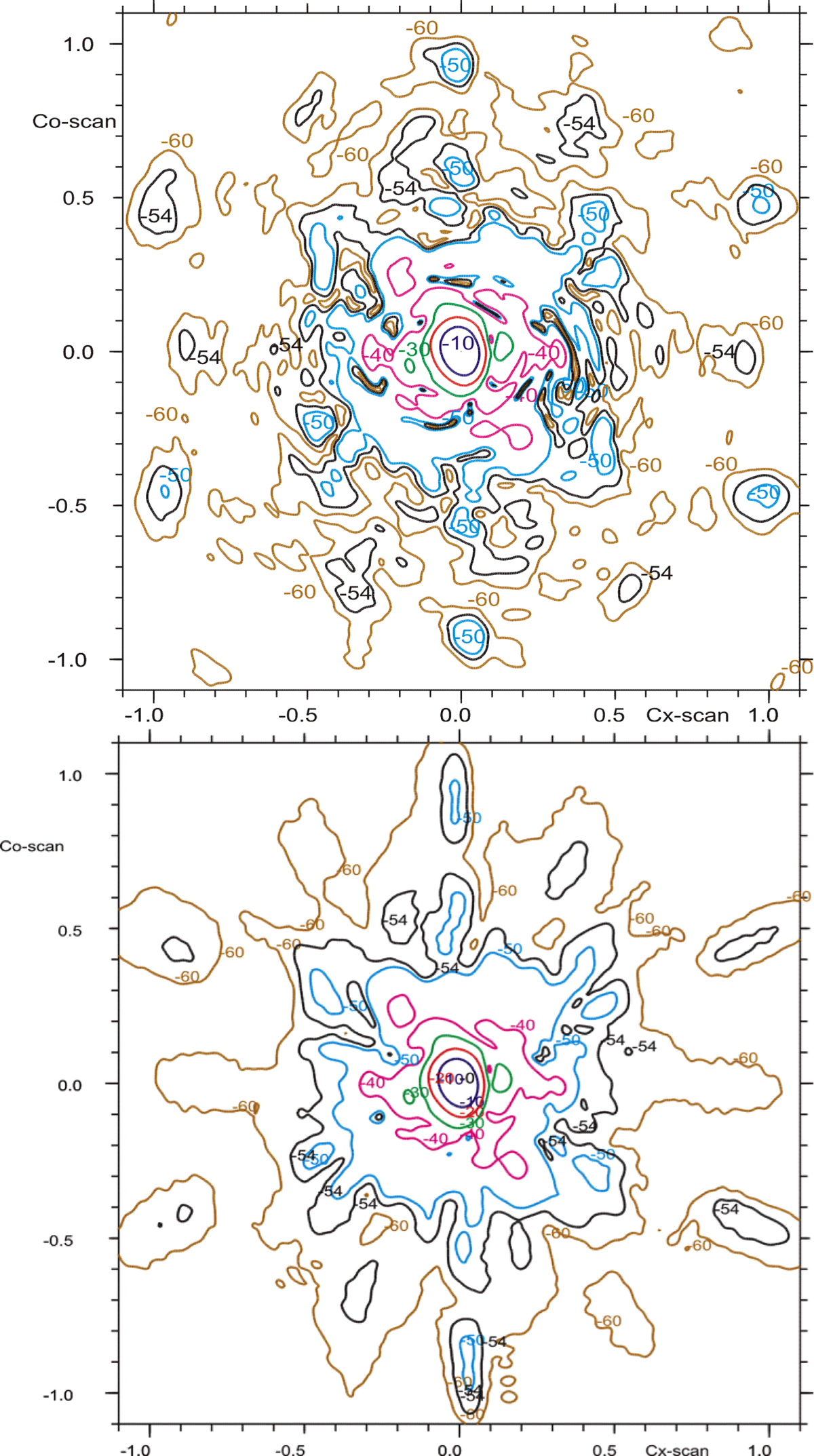
Download original image
Frequency dependence of the location of the grating lobes. Within the wide Planck channels, the nominal effect is to elongate the lobes radially and reduce their peak levels. This effect is particularly visible in the M52 lobes of the beam of detector 353-1a, shown in this figure. Top panel: GRASP model, based on the RFFM plus 4 μm (2 μm) dimples on the primary (secondary) reflectors. Bottom panel: simulation of a wideband integration for the same geometry, represented by five GRASP models at equidistant frequencies within the band, and added in power. The peak of the M52 lobe is reduced by 3.5 dB. Grating lobes originating in dimples in the secondary reflector are affected very little.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


