Fig. 1.
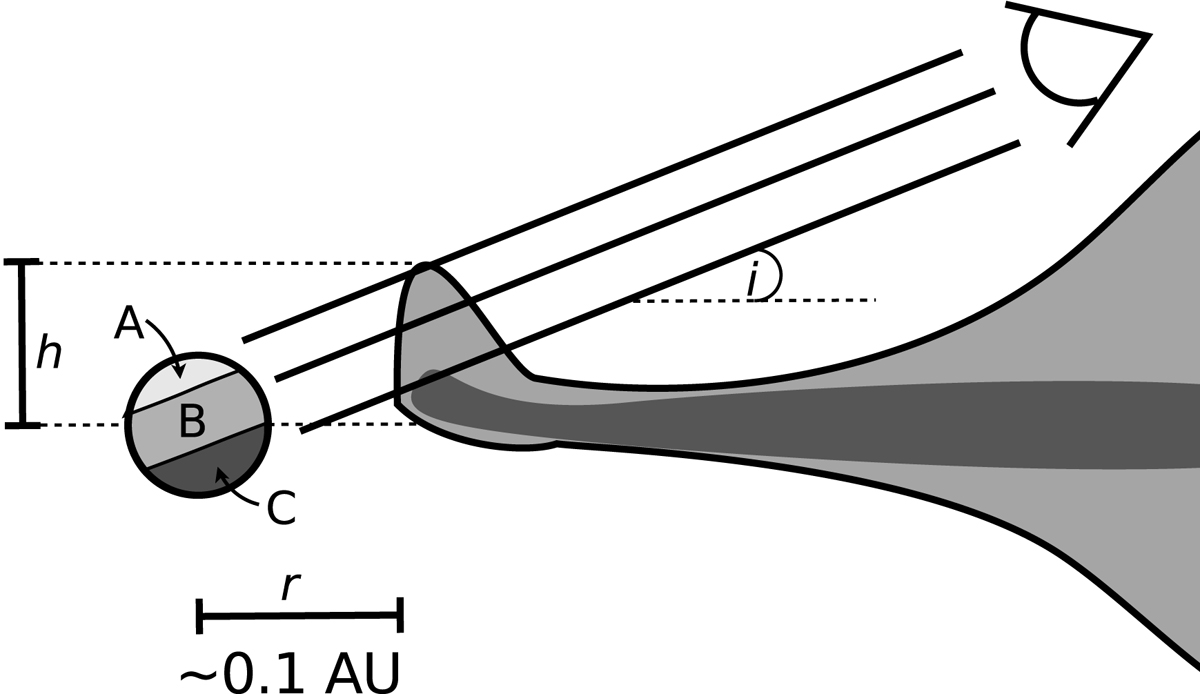
Sketch of the inner disk structure around CTTSs indicating our three component model. The unocculted part of the stellar disk is denoted with A. The upper disk layer causes reddening of part the stellar disk (part B of the stellar disk). Stellar emission from the region denoted with C is subject to opaque (gray) extinction by the lower disk layers. We also show the inner disk radius r, the viewing inclination i, and the height h of the inner disk warp with respect to the disk midplane.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


