Fig. 7
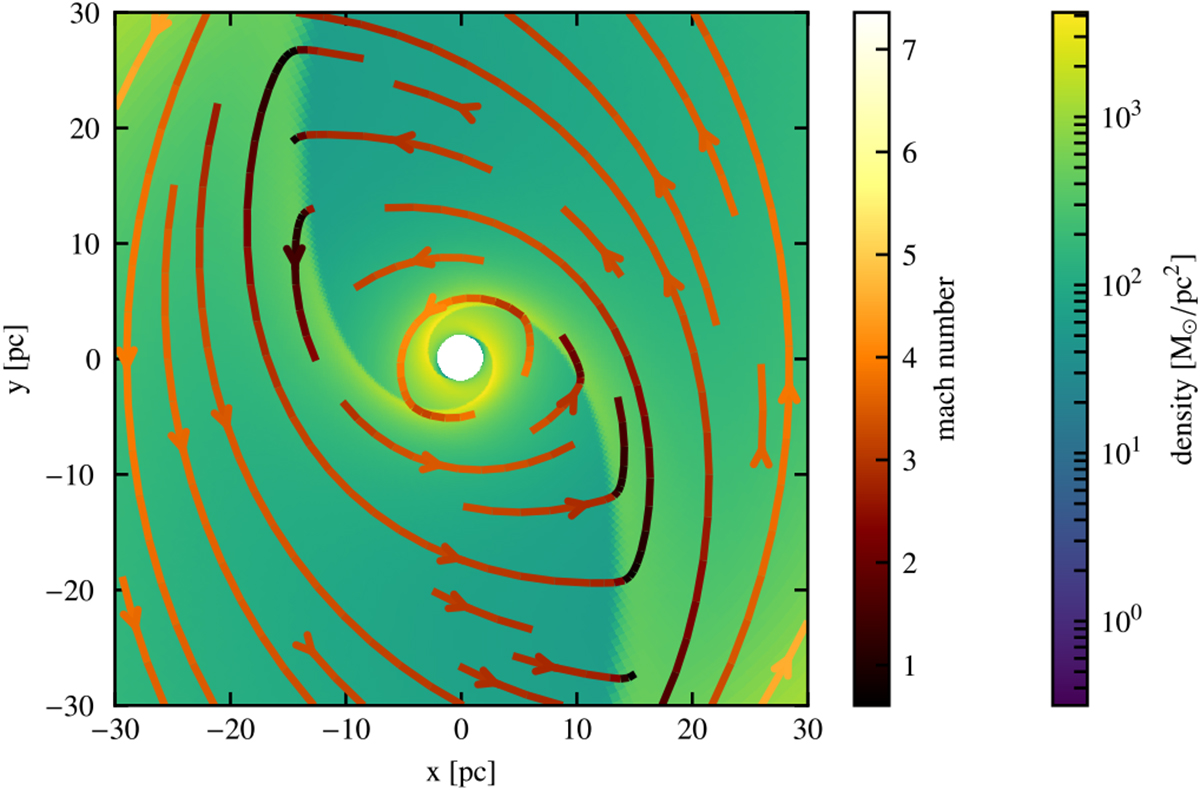
Instantaneous streamlines and surface density map of the simulation with Σ0 = 30 M⊙ pc−2 and speed of sound cs = 10 km s−1. At the shocks the gas is compressed and loses a great part of its kinetic energy. Its velocity becomes subsonic and the gas is pushed to lower radii until it again reaches sufficient velocity to balance centrifugal and gravitational forces. This process can drive the gas far into the inner disk within a few orbits.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


