Fig. 3
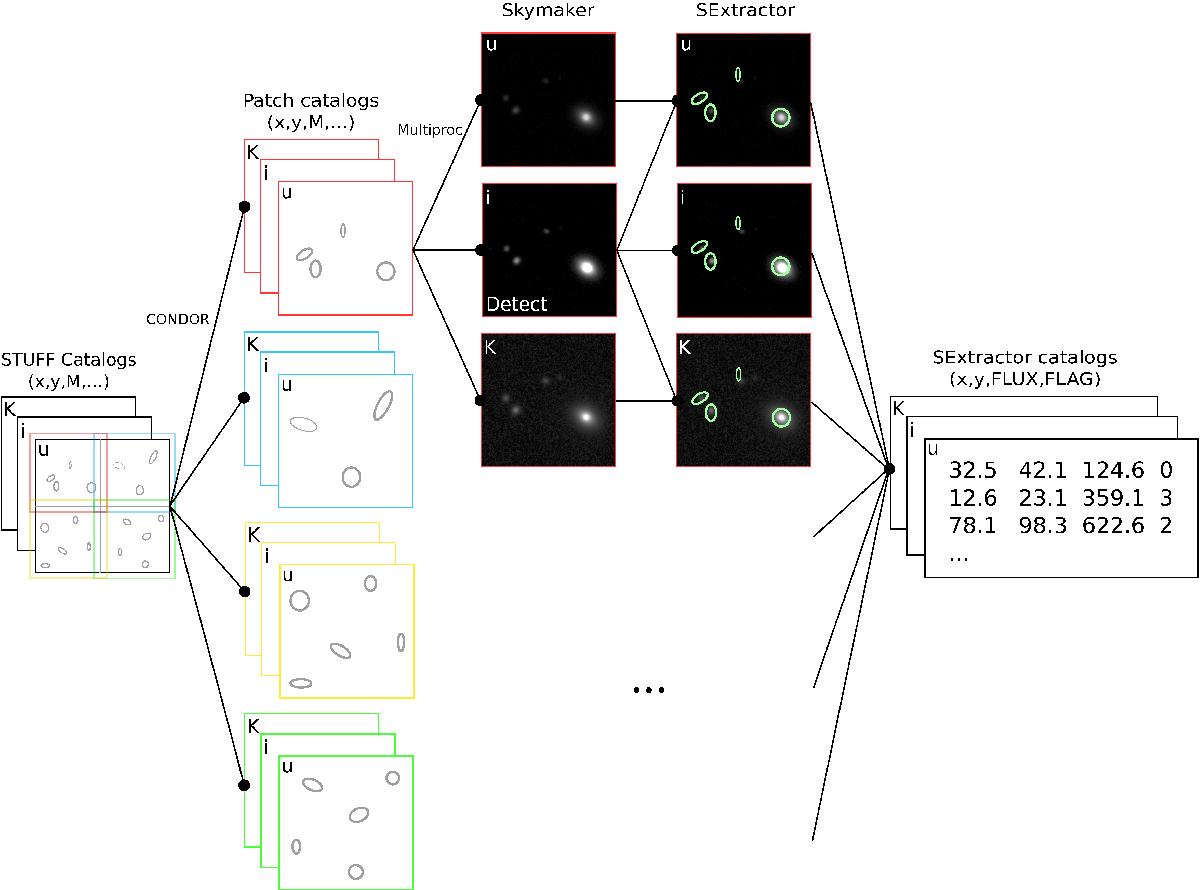
Illustration of the parallelization process of our pipeline, described in detail in Sect. 3.2. Stuff generates a catalog, that is, a set of files containing the properties of simulated galaxies, such as inclination, bulge-to-disk ratio, apparent size, and luminosity. Each file lists the same galaxies in a different passband. The parallelization process is performed on two levels: first, the Stuff catalogs are split into sub-catalogs according to the positions of the sources on the image. These sub-catalogs are sent to the nodes of the computer cluster in all filters at the same time using the HTCondor framework. Each sub-catalog is then used to generate a multiband image corresponding to a fraction of the total field. This step is multiprocessed in order to generate the patches in every band simultaneously. SExtractor is then launched on every patch synchronously, also using multiprocessing. The source detection is done in one pre-defined band, and the photometry is done in every band. Finally, the SExtractor catalogs generated from all the patches are merged into one large catalog containing the photometric and size parameters of the extracted sources from the entire field.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


