Fig. A.8
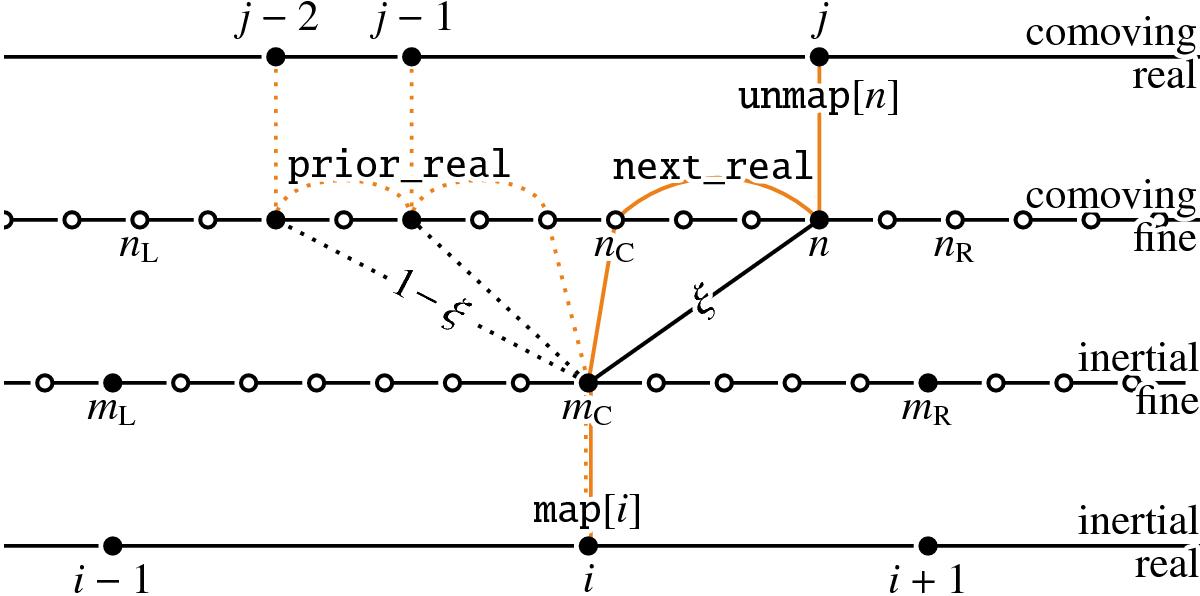
Equidistant forward interpolation from the inertial real grid onto the comoving real grid using the fine grids. Real knots (•) are marked on the real and the fine grids; virtual knots (°) are marked on the fine grids. Knots i−1, i, and i + 1 are projected from the inertial real onto inertial fine grid using the map array (mL, mC, mR) and corrected for the shift s to obtain the corresponding nearest-right neighbors nL, nC, and nR in the comoving fine grid. In the comoving fine grid, two scans with running index n are done to find real knots on the intervals [mL,mC] and [mC,mR]: from nC to nR−1 using the next_real array (solid orange line), and from nC−1 to nL using the prior_real array (dotted orange line). When a real knot is found, we find the corresponding real comoving grid index j using the unmap array. The desired l.h.s. ξ (sloped black solid line) or r.h.s. 1−ξ (sloped black dotted line) weights are computed from n, nL, nC, nR, and 4.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


